
Breaking News
 Iran (So Far Away) - Official Music Video
Iran (So Far Away) - Official Music Video
 COMEX Silver: 21 Days Until 429 Million Ounces of Demand Meets 103 Million Supply. (March Crisis)
COMEX Silver: 21 Days Until 429 Million Ounces of Demand Meets 103 Million Supply. (March Crisis)
 Marjorie Taylor Greene: MAGA Was "All a Lie," "Isn't Really About America or the
Marjorie Taylor Greene: MAGA Was "All a Lie," "Isn't Really About America or the
 Why America's Two-Party System Will Never Threaten the True Political Elites
Why America's Two-Party System Will Never Threaten the True Political Elites
Top Tech News
 How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
 Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
 Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
Iron-fortified lumber could be a greener alternative to steel beams
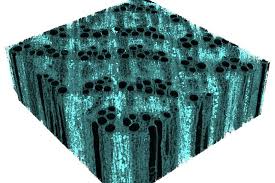
Scientists have now set about addressing that shortcoming, by strengthening wood with added iron.
Led by Asst. Prof. Vivian Merk, a team of researchers at Florida Atlantic University (FAU) started out with cubes of untreated red oak hardwood. Red oak – along with hardwoods like maple, cherry and walnut – is an example of what's known as ring-porous wood. In a nutshell, this means that it utilizes large ring-shaped internal vessels to draw water up from the tree's roots to its leaves.
The scientists proceeded to mix ferric nitrate with potassium hydroxide, creating a hard iron oxide mineral called nanocrystalline ferrihydrite, which occurs naturally in soil and water. Utilizing a vacuum impregnation process, nanoparticles of that ferrihydrite were drawn into the wood and deposited inside of its individual cell walls.



