
Breaking News
 Team USA Freestyle Skiers Express 'Mixed Emotions' and 'Heartbreak'...
Team USA Freestyle Skiers Express 'Mixed Emotions' and 'Heartbreak'...
 The Safety Cult is Going to Kill Us All
The Safety Cult is Going to Kill Us All
 10 Things I Learned From the Epstein Files
10 Things I Learned From the Epstein Files
 He's EXPOSING the truth about SSRI's and Anti-Depressants, and they are P*SSED
He's EXPOSING the truth about SSRI's and Anti-Depressants, and they are P*SSED
Top Tech News
 How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
 Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
 Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
New technique gives robotic faces living human skin
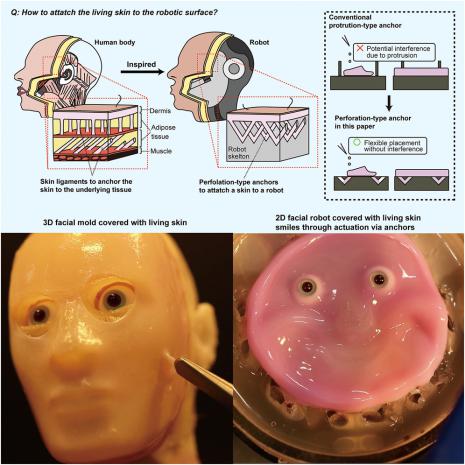
Two years ago, Prof. Shoji Takeuchi and colleagues at the University of Tokyo successfully covered a motorized robotic finger with a bioengineered skin made from live human cells.
It was hoped that this proof-of-concept exercise might pave the way not only for more lifelike android-type robots, but also for bots with self-healing, touch-sensitive coverings. The technology could additionally be used in the testing of cosmetics, and the training of plastic surgeons.
While the skin-covered finger was certainly an impressive achievement, the skin wasn't connected to the underlying digit in any way – it was basically a shrink-to-fit sheath that enveloped the finger. By contrast, natural human skin is connected to the underlying muscle tissue by ligaments.
Among other things, this arrangement allows us to exhibit our various facial expressions. Additionally, by moving along with the underlying tissue, our skin doesn't impede movement by bunching up. For this same reason, it's also less likely to be damaged by getting snagged on external objects.
Scientists have previously attempted to connect bioengineered skin to synthetic surfaces, typically via tiny anchors that protrude up from those surfaces. These pokey anchors detract from the skin's appearance, however, keeping it from looking smooth. They also don't work well on concave surfaces, where they all point in towards the middle.
With such limitations in mind, Takeuchi and his team recently developed a new skin-anchoring system based on tiny V-shaped perforations made in the synthetic surface.
The scientists created a human facial mold that incorporated an array of these perforations, then coated that mold with a gel consisting of collagen and human dermal fibroblasts. The latter are cells which are responsible for producing connective tissue in the skin.
Some of the gel flowed down into the perforations, while the rest stayed on the surface of the mold. After being left to culture for seven days, the gel formed into a covering of human skin that was securely anchored to the mold via the tissue within the perforations.



