
Breaking News
 BlackRock Slashes Another Private Loan Value From 100 To Zero
BlackRock Slashes Another Private Loan Value From 100 To Zero
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 While the Middle East burns, the U.S. just quietly launched military operations in Ecuador.
While the Middle East burns, the U.S. just quietly launched military operations in Ecuador.
Top Tech News
 US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
 Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
 H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
 We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
 She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
 A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
 DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
 Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
 WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
3D color X-ray machine heads for trials
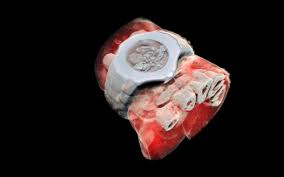
But this new scanner adds color and a third dimension, creating high resolution, cutaway 3D models that can diagnose bone fractures and monitor healing. New Zealand-based Mars Bioimaging (MBI) has now conducted a feasibility study of the machine, with a larger international trial set to begin soon.
In a traditional CT scan, X-rays are beamed through the target area of the body, and the radiation is absorbed more readily by denser tissues like bone, while passing more easily through softer tissues. The end result is that high contrast black-and-white image we know so well.
But the new technology collects more nuanced data about how the X-rays are absorbed by different tissues. It's built around a chip called the Medipix3, which tracks every photon that hits every pixel on the sensor, and processes their interactions with various atoms in the body. By doing so, it can determine the density and composition of those tissues more accurately.

 RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?
RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?

