
Breaking News
 China, India, US... 'the balance of power is changing': Musk
China, India, US... 'the balance of power is changing': Musk
 Cuba feels the pinch as US oil pressure drives food costs, blackouts and fuel shortages
Cuba feels the pinch as US oil pressure drives food costs, blackouts and fuel shortages
 ARGENTINA: Milei's Chainsaw Economic Model and The Illusion of Recovery
ARGENTINA: Milei's Chainsaw Economic Model and The Illusion of Recovery
 80,000 Toxins Every Day!! - The Deadly Truth About Your Food, Water, Skincare & Morning Joe!!
80,000 Toxins Every Day!! - The Deadly Truth About Your Food, Water, Skincare & Morning Joe!!
Top Tech News
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
 Lab–grown LIFE takes a major step forward – as scientists use AI to create a virus never seen be
Lab–grown LIFE takes a major step forward – as scientists use AI to create a virus never seen be
 New Electric 'Donut Motor' Makes 856 HP but Weighs Just 88 Pounds
New Electric 'Donut Motor' Makes 856 HP but Weighs Just 88 Pounds
 Donut Lab Says It Cracked Solid-State Batteries. Experts Have Questions.
Donut Lab Says It Cracked Solid-State Batteries. Experts Have Questions.
 Researchers who discovered the master switch that prevents the human immune system...
Researchers who discovered the master switch that prevents the human immune system...
Google switches on first-of-its-kind advanced geothermal project
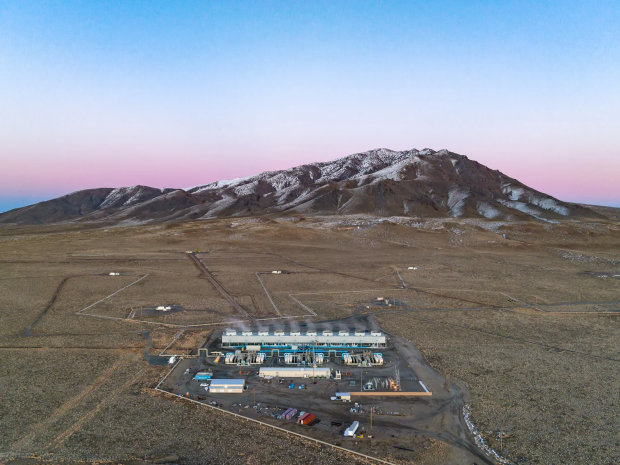

Where most geothermal projects need to seek out areas where highly-fractured, highly-permeable hot rocks are easy to get to, the Nevada plant, built in partnership with Fervo, is a pilot to prove a technique borrowed from the oil and gas industry.
As we wrote when Fervo announced its test results in July, the idea is to do for geothermal what fracking did for oil and gas, opening up resources that would otherwise be inaccessible. The company does this by drilling horizontally into deep rock, then injecting pressurized fluid to fracture the rock, creating the kind of fractured, permeable rock you need to harvest geothermal heat energy.
It's a technique Fervo says can also help get a lot more out of an existing resource, and it radically reduces one of the biggest risks in geothermal energy: the risk of drilling way down into subterranean resources and finding they're not usable.
The Nevada plant makes a constant 3.4 megawatts of energy, bringing water up from 3,250-ft-long (990-m) horizontal bores some 8,000 ft (2,440 m) below the surface, at temperatures up to 191 °C (376 °F).
Google originally saw this project as a way to do two things. Firstly, to advance its own progress toward its stated goal of operating solely on clean energy by 2030. And secondly, as a way to give Fervo a commercial jump-start – a proof of concept it could use to accelerate the uptake of advanced geothermal.
And maybe on the second goal, it's made an impressive start. In September, Fervo broke ground on another, much larger project in Utah. The Cape Station project, scheduled for grid connection in 2026 and full-scale power production by 2028, scales things up considerably. It's aiming to produce around 400 MW of energy around the clock.

 The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives

