
Breaking News
 Sunday FULL SHOW: Newly Released & Verified Epstein Files Confirm Globalists Engaged...
Sunday FULL SHOW: Newly Released & Verified Epstein Files Confirm Globalists Engaged...
 Fans Bash Bad Bunny's 'Boring' Super Bowl Halftime Show, Slam Spanish Language Performan
Fans Bash Bad Bunny's 'Boring' Super Bowl Halftime Show, Slam Spanish Language Performan
 Trump Admin Refuses To Comply With Immigration Court Order
Trump Admin Refuses To Comply With Immigration Court Order
 U.S. Government Takes Control of $400M in Bitcoin, Assets Tied to Helix Mixer
U.S. Government Takes Control of $400M in Bitcoin, Assets Tied to Helix Mixer
Top Tech News
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
 Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Mice with diabetes "functionally cured" using new stem cell therapy
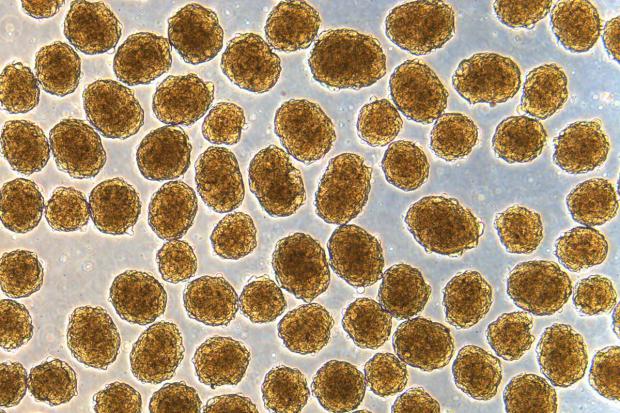
Now, scientists have developed a more efficient method of doing just that, and found that implanting these cells in diabetic mice functionally cured them of the disease.
The study builds on past research by the same team, led by Jeffrey Millman at Washington University. The researchers have previously shown that infusing mice with these cells works to treat diabetes, but the new work has had even more impressive results.
"These mice had very severe diabetes with blood sugar readings of more than 500 milligrams per deciliter of blood — levels that could be fatal for a person — and when we gave the mice the insulin-secreting cells, within two weeks their blood glucose levels had returned to normal and stayed that way for many months," says Millman.
Insulin is normally produced by beta cells in the pancreas, but in people with diabetes these cells don't produce enough of the hormone. The condition is usually managed by directly injecting insulin into the bloodstream when it's needed. But in recent years, researchers have found ways to convert human stem cells into beta cells, which can pick up the slack and produce more insulin.

 Smart dust technology...
Smart dust technology...

