
Breaking News
 Selling Us Rope: Palantir Is Raking In Billions From Washington
Selling Us Rope: Palantir Is Raking In Billions From Washington
 Tyson Foods Confirms Protein Switching Underway Amid Record High Beef Prices
Tyson Foods Confirms Protein Switching Underway Amid Record High Beef Prices
 Holy SH*T! Sex Offender Can't Adopt Kids--So He Bought One Instead? | Redacted w Clayton Morris
Holy SH*T! Sex Offender Can't Adopt Kids--So He Bought One Instead? | Redacted w Clayton Morris
Top Tech News
 'Robot skin' beats human reflexes, transforms grip with fabric-powered touch
'Robot skin' beats human reflexes, transforms grip with fabric-powered touch
 World's first nuclear fusion plant being built in US to power Microsoft data centers
World's first nuclear fusion plant being built in US to power Microsoft data centers
 The mitochondria are more than just the "powerhouse of the cell" – they initiate immune...
The mitochondria are more than just the "powerhouse of the cell" – they initiate immune...
 Historic Aviation Engine Advance to Unlock Hypersonic Mach 10 Planes
Historic Aviation Engine Advance to Unlock Hypersonic Mach 10 Planes
 OpenAI CEO Sam Altman Pitches Eyeball-Scanning World ID to Bankers
OpenAI CEO Sam Altman Pitches Eyeball-Scanning World ID to Bankers
 New 3D-printed titanium alloy is stronger and cheaper than ever before
New 3D-printed titanium alloy is stronger and cheaper than ever before
 What is Unitree's new $6,000 humanoid robot good for?
What is Unitree's new $6,000 humanoid robot good for?
 "No CGI, No AI, Pure Engineering": Watch Raw Footage Of 'Star Wars'-Style Speeder
"No CGI, No AI, Pure Engineering": Watch Raw Footage Of 'Star Wars'-Style Speeder
 NASA's X-59 'quiet' supersonic jet rolls out for its 1st test drive (video)
NASA's X-59 'quiet' supersonic jet rolls out for its 1st test drive (video)
 Hypersonic SABRE engine reignited in Invictus Mach 5 spaceplane
Hypersonic SABRE engine reignited in Invictus Mach 5 spaceplane
Perfect Waveforms for Optical Tweezers to Move Atoms, Molecules and Living Cells
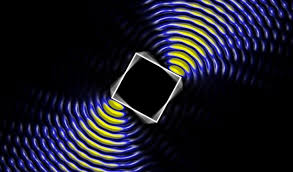
A special calculation method was developed to determine the perfect waveform to manipulate small particles in the presence of a disordered environment. This makes it possible to hold, move or rotate individual particles inside a sample – even if they cannot be touched directly. The tailor-made light beam becomes a universal remote control for everything small. Microwave experiments have already demonstrated that the method works.
Calculating the Optimal Wave
To achieve this, the particle and its disordered environment are first illuminated with various waves and the way in which the waves are reflected is measured. This measurement is carried out twice in quick succession. "Let's assume that in the short time between the two measurements, the disordered environment remains the same, while the particle we want to manipulate changes slightly," says Stefan Rotter. "Let's think of a cell that moves, or simply sinks downwards a little bit. Then the light wave we send in is reflected a little bit differently in the two measurements." This tiny difference is crucial: With the new calculation method developed at TU Wien, it is possible to calculate the wave that has to be used to amplify or attenuate this particle movement.
"If the particle slowly sinks downwards, we can calculate a wave that prevents this sinking or lets the particle sink even faster," says Stefan Rotter. "If the particle rotates a little bit, we know which wave transmits the maximum angular momentum – we can then rotate the particle with a specially shaped light wave without ever touching it."



