
Breaking News
 Grand Theft World Podcast 273 | Goys 'R U.S. with Guest Rob Dew
Grand Theft World Podcast 273 | Goys 'R U.S. with Guest Rob Dew
 Anchorage was the Receipt: Europe is Paying the Price… and Knows it.
Anchorage was the Receipt: Europe is Paying the Price… and Knows it.
 The Slow Epstein Earthquake: The Rupture Between the People and the Elites
The Slow Epstein Earthquake: The Rupture Between the People and the Elites
 Israeli Prime Minister, Netanyahu will meet with Trump on Wednesday and deliver instructions...
Israeli Prime Minister, Netanyahu will meet with Trump on Wednesday and deliver instructions...
Top Tech News
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
Embryo Breakthrough: Artificial Human Life Now Possible In Lab
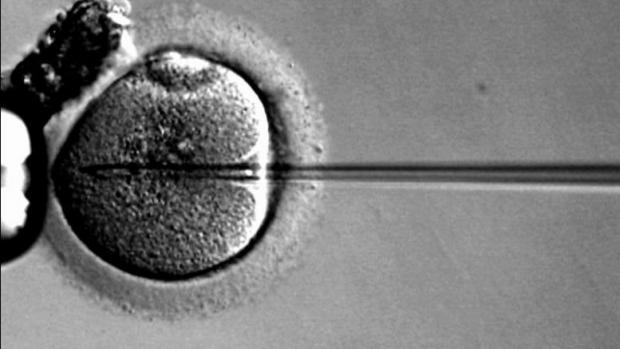
Cambridge University mixed two kinds of mouse stem cells and placed them on a 3D scaffold. After four days of growth in a tank of chemicals designed to mimic conditions inside the womb, the cells formed the structure of a living mouse embryo.
The breakthrough has been described as a 'masterpiece' in bioengineering, which could eventually allow scientists to grow artificial human embryos in the lab without the need for a sperm or an egg.
Growing embryos would help researchers to study the very early stages of human life so they could understand why so many pregnancies fail, but is likely to prove controversial and raise ethical questions about what constitutes human life.
urrently scientists can carry out experiments on leftover embryos from IVF treatments, but they are in short supply and must be destroyed after 14 days. Scientists say that being able to create unlimited numbers of artificial embryos in the lab could speed up research while potentially removing some of the ethical boundaries.



