
Breaking News
 Still No Justice for COVID Nursing Home Deaths
Still No Justice for COVID Nursing Home Deaths
 How To Make A FREE Drip Irrigation System With An Old 5 Gallon Bucket
How To Make A FREE Drip Irrigation System With An Old 5 Gallon Bucket
 Homemade LMNT Electrolyte Drink | ACTUALLY Hydrate Yourself!
Homemade LMNT Electrolyte Drink | ACTUALLY Hydrate Yourself!
Top Tech News
 Cab-less truck glider leaps autonomously between road and rail
Cab-less truck glider leaps autonomously between road and rail
 Can Tesla DOJO Chips Pass Nvidia GPUs?
Can Tesla DOJO Chips Pass Nvidia GPUs?
 Iron-fortified lumber could be a greener alternative to steel beams
Iron-fortified lumber could be a greener alternative to steel beams
 One man, 856 venom hits, and the path to a universal snakebite cure
One man, 856 venom hits, and the path to a universal snakebite cure
 Dr. McCullough reveals cancer-fighting drug Big Pharma hopes you never hear about…
Dr. McCullough reveals cancer-fighting drug Big Pharma hopes you never hear about…
 EXCLUSIVE: Raytheon Whistleblower Who Exposed The Neutrino Earthquake Weapon In Antarctica...
EXCLUSIVE: Raytheon Whistleblower Who Exposed The Neutrino Earthquake Weapon In Antarctica...
 Doctors Say Injecting Gold Into Eyeballs Could Restore Lost Vision
Doctors Say Injecting Gold Into Eyeballs Could Restore Lost Vision
 Dark Matter: An 86-lb, 800-hp EV motor by Koenigsegg
Dark Matter: An 86-lb, 800-hp EV motor by Koenigsegg
 Spacetop puts a massive multi-window workspace in front of your eyes
Spacetop puts a massive multi-window workspace in front of your eyes
Scientists Re-Engineer The Brain To Alter Human Addiction
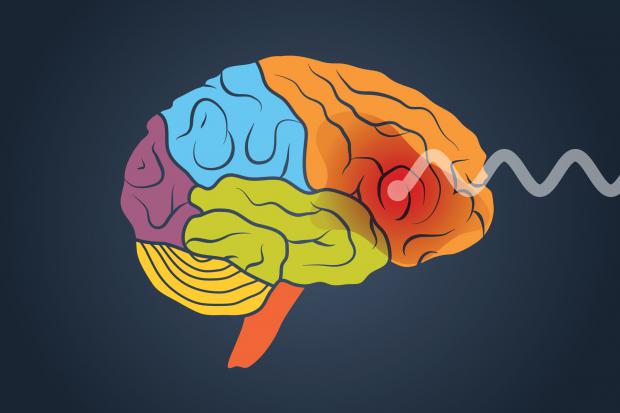
Yet, through his research into Parkinson's disease, he began to realise that – thanks to these monkeys – he might have a unique window into the brain pathways of addiction and ways of reshaping them for the better.
"I strongly believe that we have to view all brain disorders, such as addictions, through the lens of different wiring," he says. "The brain is incredible at organising connections, but certain individuals are more predisposed to being wired in certain ways."
Both Parkinson's and addictions are intrinsically linked to a substance called dopamine, often known as the pleasure chemical. Activities such as sex, drinking, taking illicit drugs, winning £10 on a slot machine or watching pornography all flood the brain with surges of dopamine, creating a desire to repeat the experience.
Some people are particularly susceptible to swiftly becoming dependent on these dopamine surges, which can subsequently develop into an addiction. When these behaviours turn into chronic habits, the brain starts to produce less and less dopamine each time, which is why addicts often explain that their drinking or drug use does not actually provide them with any pleasure.
Parkinson's, a disease which gradually kills off dopamine-producing cells in the brain, is very different, but many of the latest therapeutic approaches utilise ingenious ideas for replacing the lost dopamine. One particular therapy being studied involves delivering the gene for a protein called glial-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) into the brain, which then encourages dopamine production.

 DId Congress Kill DOGE?
DId Congress Kill DOGE?
 Node without Consent
Node without Consent

