
Breaking News
 China Will Close the Semiconductor Gap After EUV Lithography Breakthrough
China Will Close the Semiconductor Gap After EUV Lithography Breakthrough
 The Five Big Lies of Vaccinology
The Five Big Lies of Vaccinology
 Large global study analyzing data from 192 countries has sparked intense debate by suggesting...
Large global study analyzing data from 192 countries has sparked intense debate by suggesting...
Top Tech News
 EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
 This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
 Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Bionic arm allows amputees to feel with fake fingers: Prosthetic combines intuitive motor control...
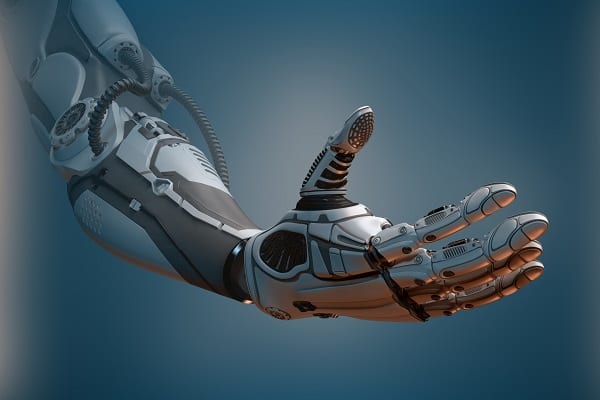
A bionic arm that combined intuitive motor control, touch and grip will allow amputees feel the sensation of feeling objects, its developers claim.
This is the first prosthetic limb that is able to test all key functions of a hand at the same time, and uses a brain-computer interface to trigger the interaction.
Lead investigator Professor Paul Marasco, of the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, said test subjects felt one of their hands was moving, even though they didn't have a hand, and felt as if their fingers were touching things, even though they had no fingers.
Putting touch, grip and motor control together, worked to trick the senses and brain of the wearer into thinking the prosthetic was a real human hand, Prof Marasco said.
It links to limb nerves which send impulses from the patient's brains to the prosthetic when they want to use or move it, and the arm receives physical information from the environment through sensors, sending it back into the brain through nerves.
The US team started out with a standard-of-care, off the shelf prosthetic arm which was then fitted with their new complex bionic system.
Tests on volunteers found that wearers could move their prosthetic arm more intuitively and feel sensations of touch and movement at the same time.
The two way communication, between brain and arm sensors, allowed the volunteers to perform a range of tasks similar to a non-amputee, they found.
'These findings are an important step towards providing people with amputation with complete restoration of natural arm function,' said Prof Marasco.

 This is why RAM costs so much
This is why RAM costs so much

