
Breaking News
 Mike Adams Fitness Update with Therapeutic PEPTIDES that Help HEAL Old Injuries
Mike Adams Fitness Update with Therapeutic PEPTIDES that Help HEAL Old Injuries
 56 Survival Uses for Heavy-Duty Garbage Bags
56 Survival Uses for Heavy-Duty Garbage Bags
 Zorro Ranch is MUCH worse than Epstein Island, the truth is coming out
Zorro Ranch is MUCH worse than Epstein Island, the truth is coming out
 We're Being DEHUMANIZED By This...
We're Being DEHUMANIZED By This...
Top Tech News
 New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
 AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
 Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
 Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
 We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Spinning Membrane Space Telescopes Would Be Big, Cheap and Easy
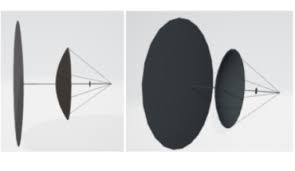
A demonstration cubesat EST could have an aperture larger than the Webb Space Telescope. The Webb Space Telescope has a 6.5-meter mirror and costs over $10 billion.
The EST employs a hoop to deploy a slack reflector membrane, such as solar sail material or radio dish. The EST is simultaneously rotated around its center and accelerated along its axis of rotation, the membrane will assume a parabolic shape, thereby creating a reflector for a very large aperture telescope. The EST reflector can be accelerated along its linear axis by tethering its deployment hoop to a tug spacecraft.
Linear acceleration will shape the telescope membrane into a parabola.
A little demonstration EST, with a total mass less than 20 kg, including optics that would be positioned along or suspended from the tether at the parabola focal point, would have four times the light gathering capacity of Webb (about thirty times that of Hubble), while costing on the order of 1/1000th as much.



