
Breaking News
 BlackRock Slashes Another Private Loan Value From 100 To Zero
BlackRock Slashes Another Private Loan Value From 100 To Zero
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 While the Middle East burns, the U.S. just quietly launched military operations in Ecuador.
While the Middle East burns, the U.S. just quietly launched military operations in Ecuador.
Top Tech News
 US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
 Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
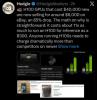 H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
 We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
 She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
 A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
 DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
 Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
 WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
Tripling Optical Storage With New Encoding Approach
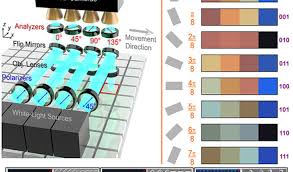
This will allow more data to be stored and for that data to be read at a quicker rate. Rather than using the traditional dots and dashes as commonly used in these technologies, the Purdue innovators encode information in the angular position of tiny antennas, allowing them to store more data per unit area.
This technology can also be used for security tagging and cryptography.
Above – The proposed anisotropic metasurface from Purdue University innovators has significant potential for high-density optical data storage, dynamic color image display, and encryption.
"The storage capacity greatly increases because it is only defined by the resolution of the sensor by which you can determine the angular positions of antennas," said Alexander Kildishev, an associate professor of electrical and computer engineering in Purdue's College of Engineering. "We map the antenna angles into colors, and the colors are decoded."

 RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?
RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?

