
Breaking News
 BlackRock Slashes Another Private Loan Value From 100 To Zero
BlackRock Slashes Another Private Loan Value From 100 To Zero
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 While the Middle East burns, the U.S. just quietly launched military operations in Ecuador.
While the Middle East burns, the U.S. just quietly launched military operations in Ecuador.
Top Tech News
 US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
 Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
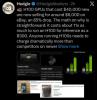 H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
 We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
 She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
 A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
 DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
 Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
 WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
Perspective on Cracking Problems With HUGE Numbers of Possibilities

Here I will describe :
* the complexity the protein folding problem. 10^300 folding possibilities for the the average protein based upon certain assumptions
* I will compare the other large problems to protein folding and some discussion about comprehending large numbers
Complexity of Protein Folding
the scale of the protein folding problem was fairly well defined and understood in 1969. Levinthal explained it.
Proteins are macromolecules which possess several unique properties. They are very large (containing 2,000 or more atoms) and complex. Their structures show no obvious regularity but a very subtle regularity is apparent upon close examination. We know from the fact that proteins may be crystallized and further from x-ray crystallography that each atom occupies a unique place in the relative 3-dimensional space of the molecule. If we consider a protein containing 2,000 atoms with no structural restrictions, such a macromolecule would possess 6,000 degrees of freedom. We know, however, from x-ray studies and other techniques as well, that there are indeed certain structural restrictions in a polypeptide structure. For example, if we schematically indicate a polypeptide chain as in Figure 1, we find that the 6 atoms in each unit indicated by the dotted lines lie in a common plane.

 RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?
RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?

