
Breaking News
 Sunday FULL SHOW: Newly Released & Verified Epstein Files Confirm Globalists Engaged...
Sunday FULL SHOW: Newly Released & Verified Epstein Files Confirm Globalists Engaged...
 Fans Bash Bad Bunny's 'Boring' Super Bowl Halftime Show, Slam Spanish Language Performan
Fans Bash Bad Bunny's 'Boring' Super Bowl Halftime Show, Slam Spanish Language Performan
 Trump Admin Refuses To Comply With Immigration Court Order
Trump Admin Refuses To Comply With Immigration Court Order
 U.S. Government Takes Control of $400M in Bitcoin, Assets Tied to Helix Mixer
U.S. Government Takes Control of $400M in Bitcoin, Assets Tied to Helix Mixer
Top Tech News
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
 Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Scientists Discover Surprising Weapon In Fight Against Brain Tumors: Ebola Virus
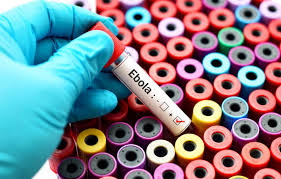
"The irony is that one of the world's deadliest viruses may be useful in treating one of the deadliest of brain cancers," comments Yale's Anthony van den Pol, professor of neurosurgery, in a release.
This unlikely medical collaboration takes advantage of a fundamental weakness in cancerous tumors. Most cancer cells are unable to defend themselves with an immune response against viruses. This fact has caused researchers to test out the use of viruses in the fight against cancer. Of course, using viruses for medical purposes carries some inherent risk; viruses can potentially lead to dangerous infections in cancer patients.
So, in an effort to mitigate that risk, the team at Yale have been experimenting with producing and testing out chimeric viruses, or artificially created viruses created using a combination of genes from various viruses. Ideally, these chimeric viruses should be able to target and attack cancer cells without actually harming or infecting patients.

 Smart dust technology...
Smart dust technology...

