
Breaking News
 Sunday FULL SHOW: Newly Released & Verified Epstein Files Confirm Globalists Engaged...
Sunday FULL SHOW: Newly Released & Verified Epstein Files Confirm Globalists Engaged...
 Fans Bash Bad Bunny's 'Boring' Super Bowl Halftime Show, Slam Spanish Language Performan
Fans Bash Bad Bunny's 'Boring' Super Bowl Halftime Show, Slam Spanish Language Performan
 Trump Admin Refuses To Comply With Immigration Court Order
Trump Admin Refuses To Comply With Immigration Court Order
 U.S. Government Takes Control of $400M in Bitcoin, Assets Tied to Helix Mixer
U.S. Government Takes Control of $400M in Bitcoin, Assets Tied to Helix Mixer
Top Tech News
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
 Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Ebola virus is no longer incurable, Congo trial reports over 90 percent success
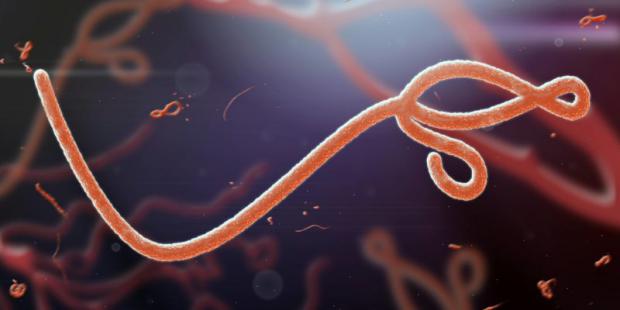
Four new treatments were being tested in the trial, but two have displayed incredible survival rates, especially if given at the earliest stages of infection.
The ongoing Ebola epidemic in Central Africa is the second worst outbreak of the virus in human history. First appearing in the Democratic Republic of the Congo in 2018, the virus has proved difficult to contain due to continuing military conflicts in the region.
Experimental vaccines have been distributed in the affected regions, however these preventative measures are of limited value in areas where the virus has already spread. In late 2018 a new clinical trial began, spanning four towns stricken by the virus. The study compared the efficacy of four different experimental treatments, but two drugs in particular have quickly shown incredible curative results.
So far, over 75 percent of those infected with the virus have died in this ongoing outbreak. The two most successful experimental drugs tested in the new trial reported significant reductions in mortality rates. The most effective agent, called REGN-EB3, showed mortality rates of only 29 percent in those treated. And even more impressively, 94 percent of those patients treated with REGN-EB3 in the earliest stage of viral infection survived.
Due to the unique nature of running a trial such as this in the middle of an ongoing outbreak, there had been an early stopping criterion built into the study in the case of a certain treatment revealing significantly positive efficacy. An independent monitoring board reviewing data from the trial recently met and decided REGN-EB3 had crossed this threshold of success resulting in the general trial being terminated.

 Smart dust technology...
Smart dust technology...

