
Breaking News
 Sunday FULL SHOW: Newly Released & Verified Epstein Files Confirm Globalists Engaged...
Sunday FULL SHOW: Newly Released & Verified Epstein Files Confirm Globalists Engaged...
 Fans Bash Bad Bunny's 'Boring' Super Bowl Halftime Show, Slam Spanish Language Performan
Fans Bash Bad Bunny's 'Boring' Super Bowl Halftime Show, Slam Spanish Language Performan
 Trump Admin Refuses To Comply With Immigration Court Order
Trump Admin Refuses To Comply With Immigration Court Order
 U.S. Government Takes Control of $400M in Bitcoin, Assets Tied to Helix Mixer
U.S. Government Takes Control of $400M in Bitcoin, Assets Tied to Helix Mixer
Top Tech News
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
 Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Two new studies strengthen the gut-brain connection in autism
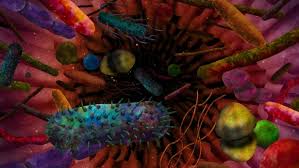
The new research reveals how gastrointestinal problems can be triggered by the same gene mutations associated with autism, and a striking mouse study has demonstrated how a fecal transplant from humans with autism can promote autism-like behaviors in the animals.
One of the more intriguing areas of microbiome research is the growing connection between gut bacteria and autism. Several recent, albeit small, studies have revealed behavioral and psychological symptoms of autism in children can be improved using fecal transplants from healthy subjects. Exactly how the microbiome could be influencing autism symptoms is still unclear but one new study, led by researchers from Caltech, has strengthened this intriguing gut-brain hypothesis.
The research began by taking microbiome samples from human subjects, both with and without autism, which were then transplanted into germ-free mice. The results were striking, with the animals receiving gut bacteria from human subjects with autism displaying hallmark autistic behaviors such as decreased social interactions and increased repetitive behaviors. The mice administered with gut bacteria from non-autistic human donors did not display these behavioral symptoms.

 Smart dust technology...
Smart dust technology...

