
Breaking News
 Col. Macgregor Gets Angry: "STOP LYING TO YOUR AUDIENCE"
Col. Macgregor Gets Angry: "STOP LYING TO YOUR AUDIENCE"
 4 Out of 5 Big Banks Are Halting Credit - Canada's Crash Deepens
4 Out of 5 Big Banks Are Halting Credit - Canada's Crash Deepens
 In a World of Chaos, Let's Talk Solutions
In a World of Chaos, Let's Talk Solutions
 Malifornia: Millennials Are Fleeing The State In Massive Numbers
Malifornia: Millennials Are Fleeing The State In Massive Numbers
Top Tech News
 1,000 miles: EV range world record demolished ... by a pickup truck
1,000 miles: EV range world record demolished ... by a pickup truck
 Fermented Stevia Extract Kills Pancreatic Cancer Cells In Lab Tests
Fermented Stevia Extract Kills Pancreatic Cancer Cells In Lab Tests
 3D printing set to slash nuclear plant build times & costs
3D printing set to slash nuclear plant build times & costs
 You can design the wheels for NASA's next moon vehicle with the 'Rock and Roll Challenge
You can design the wheels for NASA's next moon vehicle with the 'Rock and Roll Challenge
 'Robot skin' beats human reflexes, transforms grip with fabric-powered touch
'Robot skin' beats human reflexes, transforms grip with fabric-powered touch
 World's first nuclear fusion plant being built in US to power Microsoft data centers
World's first nuclear fusion plant being built in US to power Microsoft data centers
 The mitochondria are more than just the "powerhouse of the cell" – they initiate immune...
The mitochondria are more than just the "powerhouse of the cell" – they initiate immune...
 Historic Aviation Engine Advance to Unlock Hypersonic Mach 10 Planes
Historic Aviation Engine Advance to Unlock Hypersonic Mach 10 Planes
 OpenAI CEO Sam Altman Pitches Eyeball-Scanning World ID to Bankers
OpenAI CEO Sam Altman Pitches Eyeball-Scanning World ID to Bankers
 New 3D-printed titanium alloy is stronger and cheaper than ever before
New 3D-printed titanium alloy is stronger and cheaper than ever before
$1 Million Prize Offered to Israeli Moon Lander Mission
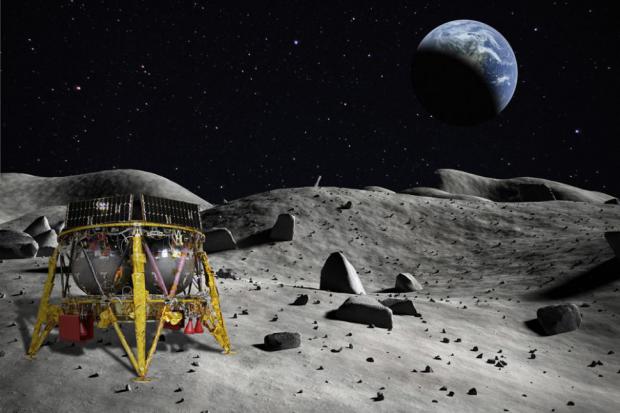

The stakes just got even higher for an Israeli moon lander's historic touchdown attempt next month.
If all goes according to plan on April 11, the robotic lander, known as Beresheet, will become the first privately funded craft ever to pull off a soft lunar touchdown. To date, only the governments of the Soviet Union, the United States and China have landed missions on the moon.
Success will also net Beresheet's builders — the nonprofit group SpaceIL and the company Israel Aerospace Industries — a cool $1 million, courtesy of the X Prize Foundation.
"SpaceIL's mission represents the democratization of space exploration," X Prize founder and Executive Chairman Peter Diamandis said in a statement today (March 28) announcing this "Moonshot Award."
"We are optimistic about seeing this first domino fall, setting off a chain reaction of increasingly affordable and repeatable commercial missions to the moon and beyond," Diamandis added. (Beresheet's total mission cost, including launch, is about $100 million, team members have said.)
The nonprofit X Prize Foundation operates big-purse competitions designed to spur technological breakthroughs in a variety of fields. One such event was the Google Lunar X Prize (GLXP), a $30 million contest that challenged privately funded teams to land a robot on the moon, move the craft at least 1,650 feet (500 meters) on the lunar surface and have it beam high-resolution imagery home to Earth.
The GLXP ended last year without a winner, but several former entrants have continued to develop their robotic moon missions. One of them is SpaceIL, which was founded in 2011 to compete for the prize.
Read More...



