
Breaking News
 Sunday FULL SHOW: Newly Released & Verified Epstein Files Confirm Globalists Engaged...
Sunday FULL SHOW: Newly Released & Verified Epstein Files Confirm Globalists Engaged...
 Fans Bash Bad Bunny's 'Boring' Super Bowl Halftime Show, Slam Spanish Language Performan
Fans Bash Bad Bunny's 'Boring' Super Bowl Halftime Show, Slam Spanish Language Performan
 Trump Admin Refuses To Comply With Immigration Court Order
Trump Admin Refuses To Comply With Immigration Court Order
 U.S. Government Takes Control of $400M in Bitcoin, Assets Tied to Helix Mixer
U.S. Government Takes Control of $400M in Bitcoin, Assets Tied to Helix Mixer
Top Tech News
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
 Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
AnAge database of animal longevity and other aging databases
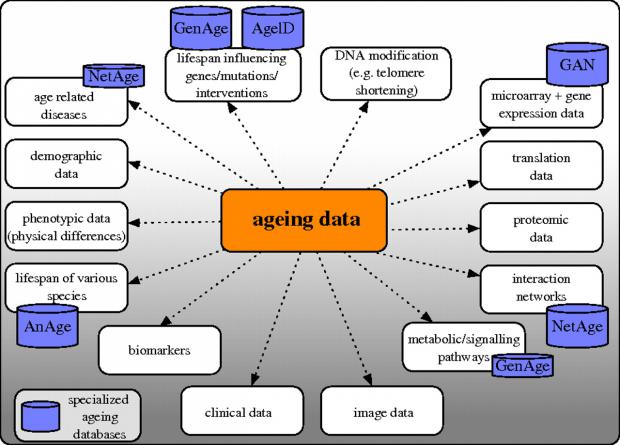
AnAge was primarily developed for comparative biology studies, in particular studies of longevity and aging, but can also be useful for ecological and conservation studies and as a reference for zoos and field biologists.
It can be used to find outlier animals with unusual longevity.
The ocean quahog (Arctica islandica) is a species of edible clam. Arctica islandica resembles the quahog, but the shell of the ocean quahog is rounder, the periostracum is usually black, and on the interior of the shell, the pallial line has no indentation, or sinus. Unlike the quahog, which lives intertidally and can be collected by clam digging, this species lives subtidally, and can only be collected by dredging. They grow to sizes exceeding 50 mm shell height. An individual specimen was reported to have lived 507 years.

 Smart dust technology...
Smart dust technology...

