
Breaking News
 Ultimate House of Cards: $5.1 Trillion Bond Fraud Set to Dwarf 2008 Crisis
Ultimate House of Cards: $5.1 Trillion Bond Fraud Set to Dwarf 2008 Crisis
 Escalation of Force: How to Choose the Appropriate Response to Potential Violence
Escalation of Force: How to Choose the Appropriate Response to Potential Violence
 Epstein's Island And The Gateway To The Psychology Of Evil
Epstein's Island And The Gateway To The Psychology Of Evil
 The Epstein Emails Reveal Shadow 9/11 Commission – Exclusive Report!
The Epstein Emails Reveal Shadow 9/11 Commission – Exclusive Report!
Top Tech News
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
 Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
3D-printed nerve stem cells could help patch up spinal cord injuries
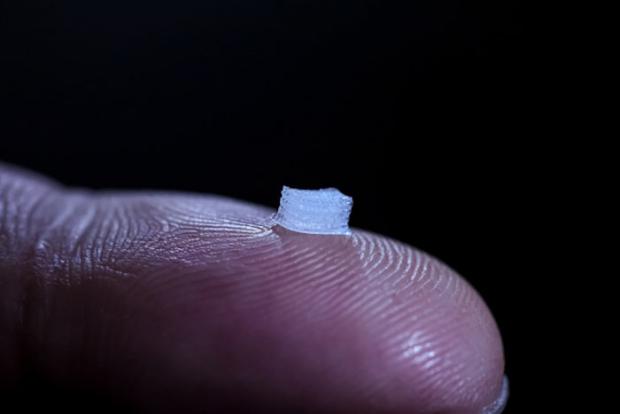
Now, researchers at the University of Minnesota have designed a device that could link everything back together again. A silicone guide, covered in 3D-printed neuronal stem cells, can be implanted into the injury site, where it grows new connections between remaining nerves to let patients regain some motor control.
A damaged spinal cord is a difficult injury to patch up, but there are treatments in development. Gene therapy could help break down scar tissue and regenerate nerve cells. In other cases the injury site is bypassed altogether, rerouting messages from the brain through computers or sending the signals wirelessly to a device implanted in the lower part of the body.

 Smart dust technology...
Smart dust technology...

