
Breaking News
 China's Nightmarish New Bio Weapon Targets Race and Ethnicity
China's Nightmarish New Bio Weapon Targets Race and Ethnicity
 The Epstein Files Just EXPOSED the AI Mind Control Agenda (2026 Warning)
The Epstein Files Just EXPOSED the AI Mind Control Agenda (2026 Warning)
 Maxwell offers testimony if granted Trump clemency
Maxwell offers testimony if granted Trump clemency
 How RFK Jr's Guidelines Could Change Farming - Joel Salatin
How RFK Jr's Guidelines Could Change Farming - Joel Salatin
Top Tech News
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
 Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Diagnostic device uses smartphone to check almost 100 samples at once
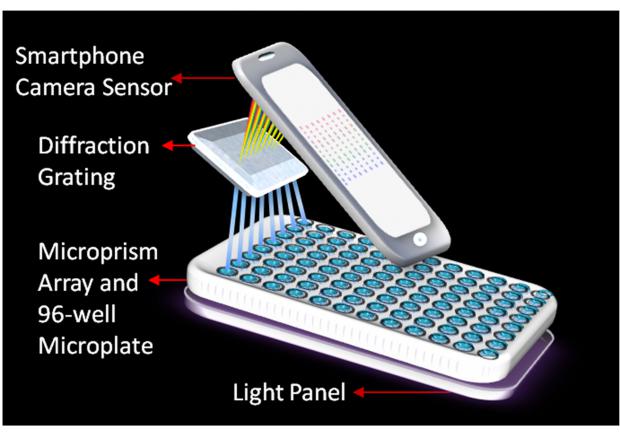
Most such devices, however, can only analyze individual samples. By contrast, a new one can check 96 samples for diseases, all at one time.
Known as the mReader, the portable device was designed by a Washington State University team led by assistant professor Lei Li, working in collaboration with the University of Pennsylvania's associate professor Ping Wang.
It contains 96 sample wells, each one of which can be loaded with fluid samples from individual patients. Users add a reagent to those samples, causing them to change to a specific color if a target biomarker is present. A smartphone mounted on the device then takes a photo of all the samples, with a computer program subsequently analyzing the color of the samples in that photo, determining if each patient is infected with the malady in question – the program can identify 12 common viral and bacterial infectious diseases.

 Smart dust technology...
Smart dust technology...

