
Breaking News
 China's Nightmarish New Bio Weapon Targets Race and Ethnicity
China's Nightmarish New Bio Weapon Targets Race and Ethnicity
 The Epstein Files Just EXPOSED the AI Mind Control Agenda (2026 Warning)
The Epstein Files Just EXPOSED the AI Mind Control Agenda (2026 Warning)
 Maxwell offers testimony if granted Trump clemency
Maxwell offers testimony if granted Trump clemency
 How RFK Jr's Guidelines Could Change Farming - Joel Salatin
How RFK Jr's Guidelines Could Change Farming - Joel Salatin
Top Tech News
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
 Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
MIT imaging technique sheds light on the brain's electrical activity
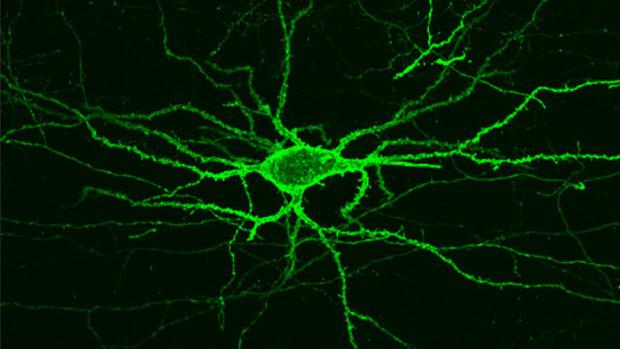
Brain MRIs offer important insight into how our brains work, but they can only produce crude approximations of the areas that are activated by a given stimulus. In order to unravel the minutiae of how neurons communicate and collaborate to form thoughts and feelings, we would need imaging tools with vastly improved resolutions.
Today, far from being able to tackle the 86 billion neurons in the human brain, neuroscientists must settle for studying simple organisms like worms and fish larvae (with neuron counts in the hundreds), relying on slow and cumbersome methods like implanting electrodes into brain tissue to detect electrical signals.
This, however, could soon change. The group of researchers led by Prof. Ed Boyden at MIT has built on previous work to perfect an imaging technique that provides a much fuller picture of the brain's activity. When exposed to red light, a carefully selected fluorescent protein bound to the cellular membrane of neurons reacts to electrical signals by lighting up, to reveal the exact neural path of a thought.

 Smart dust technology...
Smart dust technology...

