
Breaking News
 EXCLUSIVE: "The HUGE Elephant In The Room Is Actually What Jeffrey Epstein Was Best At..."
EXCLUSIVE: "The HUGE Elephant In The Room Is Actually What Jeffrey Epstein Was Best At..."
 EXCLUSIVE INTERVIEW: Republican Candidate For Texas Governor "Doc" Pete Chambers Joins...
EXCLUSIVE INTERVIEW: Republican Candidate For Texas Governor "Doc" Pete Chambers Joins...
 Epstein Files Trigger Political Fallout Across Europe
Epstein Files Trigger Political Fallout Across Europe
 Conjoined twin 'influencers' who have gained more than 280,000 followers with their intimate
Conjoined twin 'influencers' who have gained more than 280,000 followers with their intimate
Top Tech News
 How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
 Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
 Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
New desalination membrane produces both drinking water and lithium
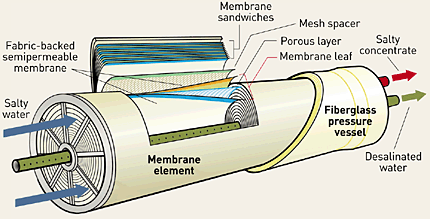
Now, a team of scientists from Australia and the US has developed a new water desalination technique that can not only make seawater fresh enough to drink, but recover lithium ions for use in batteries.
The key to the process is metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), which boast the largest internal surface area of any known material. Unfolded, a single gram of the material could theoretically cover a football field, and it's this intricate internal structure that makes MOFs perfect for capturing, storing and releasing molecules. Recent research into the material could see MOFs put to work as carbon emission sponges, high-precision chemical sensors, and urban water filters.
Currently, reverse osmosis membranes are the most commonly-used technology for water filtration, and they work on a fairly simple principle. The membrane's pores are large enough for water molecules to pass through, but too small for most contaminants.



