
Breaking News
 Israeli Prime Minister, Netanyahu will meet with Trump on Wednesday and deliver instructions...
Israeli Prime Minister, Netanyahu will meet with Trump on Wednesday and deliver instructions...
 Elon Musk Offers To Cover Legal Bills Of Epstein Survivors Who Identify New Names
Elon Musk Offers To Cover Legal Bills Of Epstein Survivors Who Identify New Names
 Red Alert Emergency Broadcast! Tune In NOW As Alex Jones Analyzes The Insane Revelations...
Red Alert Emergency Broadcast! Tune In NOW As Alex Jones Analyzes The Insane Revelations...
 330 gallons of sulphuric acid was purchased for Epstein Island on the day the FBI opened...
330 gallons of sulphuric acid was purchased for Epstein Island on the day the FBI opened...
Top Tech News
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
This Is What The First Soft Artificial Heart Looks Like
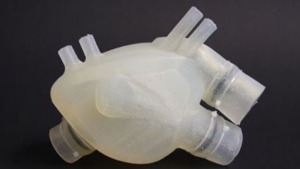
A doctoral student named Nicholas Cohrs created it along with a group from ETH Zurich using 3D printing but it's a work in progress.
"Our goal is to develop an artificial heart that is roughly the same size as the patient's own one and which imitates the human heart as closely as possible in form and function," said Cohrs.
There is still one major issue with it.
The heart only lasts about 3,000 heartbeats. That's roughly 30 to 45 minutes.
Why?
The material can't seem to stand the strain.
Despite that, it still shows the potential of artificial organs possibly saving lives in the future.
"A well-functioning artificial heart is a real necessity: about 26 million people worldwide suffer from heart failure while there is a shortage of donor hearts. Artificial blood pumps help to bridge the waiting time until a patient receives a donor heart or their own heart recovers," said Cohrs.



