
Breaking News
 Israeli Prime Minister, Netanyahu will meet with Trump on Wednesday and deliver instructions...
Israeli Prime Minister, Netanyahu will meet with Trump on Wednesday and deliver instructions...
 Elon Musk Offers To Cover Legal Bills Of Epstein Survivors Who Identify New Names
Elon Musk Offers To Cover Legal Bills Of Epstein Survivors Who Identify New Names
 Red Alert Emergency Broadcast! Tune In NOW As Alex Jones Analyzes The Insane Revelations...
Red Alert Emergency Broadcast! Tune In NOW As Alex Jones Analyzes The Insane Revelations...
 330 gallons of sulphuric acid was purchased for Epstein Island on the day the FBI opened...
330 gallons of sulphuric acid was purchased for Epstein Island on the day the FBI opened...
Top Tech News
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
Amputees can learn to control a robotic arm with their minds
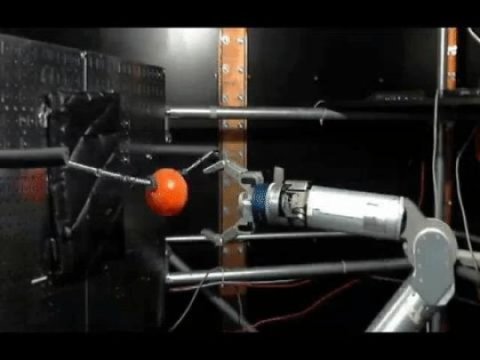
The results show both areas can create new connections to learn how to control the device, even several years after an amputation.
A new study by neuroscientists at the University of Chicago shows how amputees can learn to control a robotic arm through electrodes implanted in the brain.
The research, published in Nature Communications, details changes that take place in both sides of the brain used to control the amputated limb and the remaining, intact limb. The results show both areas can create new connections to learn how to control the device, even several years after an amputation.
"That's the novel aspect to this study, seeing that chronic, long-term amputees can learn to control a robotic limb," said Nicho Hatsopoulos, PhD, professor of organismal biology and anatomy at UChicago and senior author of the study. "But what was also interesting was the brain's plasticity over long-term exposure, and seeing what happened to the connectivity of the network as they learned to control the device."



