
Breaking News
 Poland to Buy 150 Tons More Gold, Approves up to 36.6% Held
Poland to Buy 150 Tons More Gold, Approves up to 36.6% Held
 Michael Oliver: T-Bond Nuclear Panic Will Send Silver VIOLENTLY to $300–$500 | Gold to $8,000
Michael Oliver: T-Bond Nuclear Panic Will Send Silver VIOLENTLY to $300–$500 | Gold to $8,000
 Greentanamo: Trump Deal Gives US Sovereignty Over Small Pockets Of Greenland For Military Bases
Greentanamo: Trump Deal Gives US Sovereignty Over Small Pockets Of Greenland For Military Bases
 Das: Trump's Spat With The Fed Is Not About Central Bank Independence
Das: Trump's Spat With The Fed Is Not About Central Bank Independence
Top Tech News
 The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
 'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
 Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
 XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
 Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
 Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
 NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
 Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
 The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
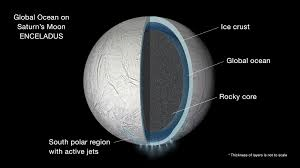
'Substantial' ocean of water beneath moon's surface could help create human colony
Researchers at Brown University in the US examined glass beads, a type of volcanic crystal gathered during the Apollo 15 and 17 missions in the 1970s, and found they contained similar volumes of water to Earth's basalt rock.
The leaders of the study, which has been published in Nature Geoscience, cite the parallels as evidence that parts of the moon contain a similarly large amount of water. This, they believe, could be useful for future lunar missions as it means water could potentially be extracted rather than carried from home.
"Other studies have suggested the presence of water ice in shadowed regions at the lunar poles, but the pyroclastic deposits are at locations that may be easier to access," said lead author Dr. Shuai Li, formerly of Brown University and now at the University of Hawaii.
"Anything that helps save future lunar explorers from having to bring lots of water from home is a big step forward, and our results suggest a new alternative."

 Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market
Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market


