
Breaking News
 Grand Theft World Podcast 273 | Goys 'R U.S. with Guest Rob Dew
Grand Theft World Podcast 273 | Goys 'R U.S. with Guest Rob Dew
 Anchorage was the Receipt: Europe is Paying the Price… and Knows it.
Anchorage was the Receipt: Europe is Paying the Price… and Knows it.
 The Slow Epstein Earthquake: The Rupture Between the People and the Elites
The Slow Epstein Earthquake: The Rupture Between the People and the Elites
 Israeli Prime Minister, Netanyahu will meet with Trump on Wednesday and deliver instructions...
Israeli Prime Minister, Netanyahu will meet with Trump on Wednesday and deliver instructions...
Top Tech News
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
Scientists have figured out how our brains sharpen our memories while we sleep
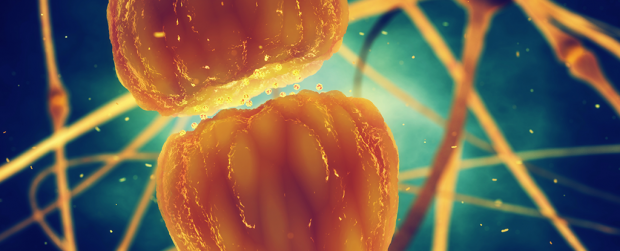
We all know that if we want what we've studied during the day to stick, it's best to get a good night's sleep. And while scientists have long understood that our memories rely on connections being built between neurons in our brains, it's not been clear how sleep actually helps to consolidate that information.
Now, two new studies have found biological evidence that expains the age-old wisdom that if we want to remember, we need to sleep to forget.
It's natural that we're curious about why we fall unconscious for up to 16 hours every day. One recent hypothesis suggested that sleep flushes out potentially toxic proteins which build up in the brain during the day.
And recent studies have found that if we don't get enough sleep, we increase our risk of developing cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes, not to mention neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson's disease.



