
Breaking News
 Iran (So Far Away) - Official Music Video
Iran (So Far Away) - Official Music Video
 COMEX Silver: 21 Days Until 429 Million Ounces of Demand Meets 103 Million Supply. (March Crisis)
COMEX Silver: 21 Days Until 429 Million Ounces of Demand Meets 103 Million Supply. (March Crisis)
 Marjorie Taylor Greene: MAGA Was "All a Lie," "Isn't Really About America or the
Marjorie Taylor Greene: MAGA Was "All a Lie," "Isn't Really About America or the
 Why America's Two-Party System Will Never Threaten the True Political Elites
Why America's Two-Party System Will Never Threaten the True Political Elites
Top Tech News
 How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
 Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
 Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
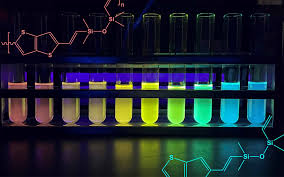
Insulator Becomes Conducting Semiconductor And Could Make Superelastic Silicone Solar Panels
On a molecular level, silicones are made up of a backbone of alternating silicon and oxygen atoms (Si—O—Si) with organic (carbon-based) groups attached to the silicon. Various 3D formations of polymer chains arise as they connect to one another, known as cross-linking, which alter the material's physical properties like strength or solubility.
This could lead to super-elastic silicone PV cells(/panels) and super-elastic thus super-durable, thick and highly energy dense lithium-ion battery anodes.
While studying different cross-linking structures in silicone, the research team stumbled upon the potential for electrical conductivity in a copolymer, which is a polymer chain containing two different types of repeating units—cage-structured and then linear silicones in this case.
The possibility for conductivity arises from the way electrons can move across Si—O—Si bonds with overlapping orbitals. Semiconductors have two main states: the ground state, which doesn't conduct electricity, and a conducting state, which does. The conducting state, also known as an excited state, occurs when some electrons jump up to the next electron orbital, which is connected across the material like a metal.
Typically, Si—O—Si bond angles don't allow for that connection. At 110°, they are a long way from a 180° straight line. But in the silicone copolymer the team discovered, these bonds started out at 140° in the ground state—and they stretch to 150° in the excited state. This was enough to create a highway for electrical charge to flow.
σ–σ* conjugation Across Si?O?Si Bonds. Macromol.
"This allows an unexpected interaction between electrons across multiple bonds including Si—O—Si bonds in these copolymers," Laine said. "The longer the chain length, the easier it is for electrons to travel longer distances, reducing the energy needed to absorb light and then emit it at lower energies."
The semiconducting properties of the silicone copolymers also enable its spectrum of colors. Electrons jump between the ground and excited states by absorbing and emitting photons, or particles of light. The light emission depends on the length of the copolymer chain, which Laine's team can control. Longer chain lengths mean smaller jumps and lower energy photons, giving the silicone a red tint. Shorter chains require bigger jumps from the electrons, so they emit higher energy light toward the blue end of the spectrum.



