
Breaking News
 Zone 00: Permaculture for the Inner Landscape (No Land Required)
Zone 00: Permaculture for the Inner Landscape (No Land Required)
 Sam Bankman-Fried files for new trial over FTX fraud charges
Sam Bankman-Fried files for new trial over FTX fraud charges
 Big Tariff Refunds Are Coming. How Much and How Soon?
Big Tariff Refunds Are Coming. How Much and How Soon?
Top Tech News
 New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
 AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
 Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
 Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
 We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
See The Human Brain Like Never Before
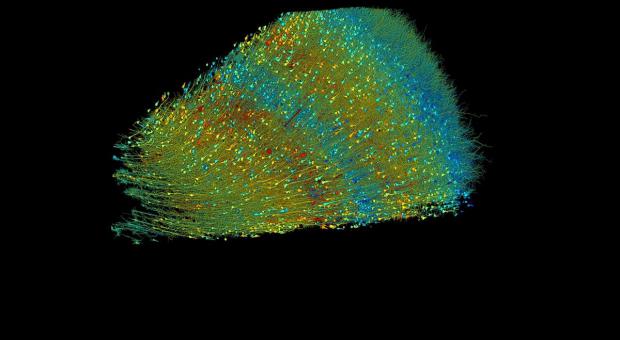
Now, after a decade of collaboration with Google scientists, a monumental dataset—with 1,400 terabytes—has turned into the most detailed map of the human brain ever created.
"A terabyte is, for most people, gigantic, yet a fragment of a human brain—just a minscule, teeny-weeny little bit of human brain—is still thousands of terabytes," Lichtman said in a National Institutes of Health report.
The detailed 3-D reconstruction reveals beautiful structures in the brain. Neurons forming dozens of connections, mirror-image neural pairs, and networks far more complex than expected, are just some of the groundbreaking discoveries.
"I remember this moment, going into the map and looking at one individual synapse from this woman's brain, and then zooming out into these other millions of pixels," said Viren Jain, a senior scientist at Google in Nature Magazine. "It felt sort of spiritual."
The map, now part of an open-access dataset online, opens the door to new understandings of human cognition, psychiatric disorders, and the architecture of our minds.
"There is the saying that 'A map of synaptic connections is necessary but insufficient to understand the brain.' In its current form it is still missing a lot of important information, but it is a step in the right direction," Daniel Berger, a scientist in the Lichtman lab, told The Epoch Times.
Excitatory neurons, color-coded by size, with red being the largest and blue the smallest. Cell cores range from 15 to 30 micrometers.
A single white neuron receives signals from more than 5,000 blue axons, with green synapses marking the points where the signals transfer.
Neurons with long dendrites and dendrite spine. In very rare cases, a single axon (blue) made repeated synaptic connections (yellow) with a target neuron (green).
One unexpected discovery in the study was the presence of "axon whorls"—tangled loops of blue axons—which typically transmit signals away from nerve cells. These structures were rare in the sample and sometimes appeared to be resting on yellow cells. Their purpose remains unclear.

 Iran & Epstein Fallout
Iran & Epstein Fallout


