
Breaking News
 If You Grew Up In The 1970s, You Probably Possess These Rare Traits
If You Grew Up In The 1970s, You Probably Possess These Rare Traits
 Silver Madness: CME Margin Spike + What It Means Next | Mike Maloney
Silver Madness: CME Margin Spike + What It Means Next | Mike Maloney
 If I Had to Start Prepping From Zero in 2026… Here's the Exact Plan (30/90/Year 1)
If I Had to Start Prepping From Zero in 2026… Here's the Exact Plan (30/90/Year 1)
22 ARC vs. 6mm ARC: Which Advanced Rifle Cartridge Is Better?
Top Tech News
 Laser weapons go mobile on US Army small vehicles
Laser weapons go mobile on US Army small vehicles
 EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
 This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Where does our 'brain waste' go? Scientists think they've figured it out and can use it.
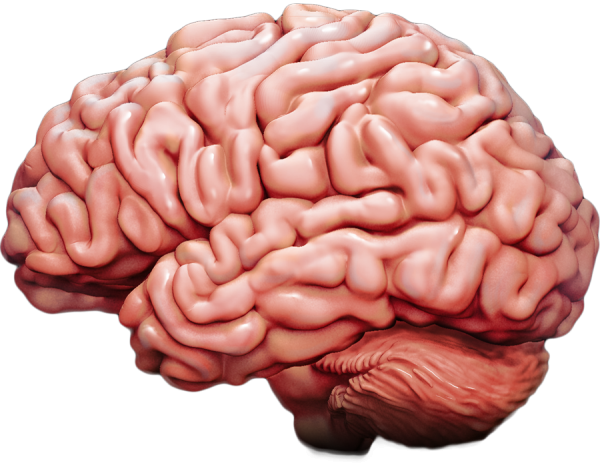
Scientists are beginning to understand how the brain flushes out waste products in order to stay healthy and fend off neurological diseases.
Two teams of scientists from Washington have uncovered signs that a slow wave of electricity that pulses through the brain during sleep pushes waste products, including the protein closely associated with Alzheimer's disease, from deep in the brain to its surface.
A vein passing through the brain then acts as a pipe to carry waste products out through the barrier that separates the brain and the rest of the body. This deposits them into the bloodstream to be filtered out by the kidneys.
But if the disposal system stops working correctly, which can occur with aging, in cases of traumatic brain injury, and chronic stress, those waste products can accumulate in the brain.
It may also allow immune cells to penetrate the organ, leading to inflammation linked to degenerative brain disorders.
The study was conducted in mice, but researchers believe their findings match up with research on potential causes of Alzheimer's disease and other dementias.
In February, scientists led by Dr Jonathan Kipnis, a neurologist at Washington University in St Louis, answered the question of how the brain gets waste out through the rigid protective barrier without using the body's lymphatic system, a network that drains fluids throughout the body.
The brain is not part of that system and its waste disposal pathway is known as the glymphatic system. It clears out waste generated by energy-consuming metabolic processes - all the chemical processes continuously working in the body to ensure it functions correctly - such as carbon dioxide, damaged proteins and dead cells.
Scientists uncovered exit points around the brain from which cerebrospinal fluid, which carries waste, flowed out to the thick membrane surrounding the brain and spinal cord and into the bloodstream, where the body's lymphatic vessels took over to clear it out.



