
Breaking News
 Who Is ?@NickShirley?? | PBD Podcast | 710
Who Is ?@NickShirley?? | PBD Podcast | 710
 20 Cozy Ways to Celebrate New Year's Eve at Home
20 Cozy Ways to Celebrate New Year's Eve at Home
 The methylation switch: Scientists identify diet that can turn back the cellular clock
The methylation switch: Scientists identify diet that can turn back the cellular clock
 Americans are slaves for the wealthy elite's that write legislation along side corporations...
Americans are slaves for the wealthy elite's that write legislation along side corporations...
Top Tech News
 Laser weapons go mobile on US Army small vehicles
Laser weapons go mobile on US Army small vehicles
 EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
 This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
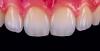 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Science shocker: Light can vaporize water without heat, says MIT study

For millennia, humans have observed and utilized evaporation, the process by which water transforms from a liquid to a vapor. From witnessing the sun's dry morning fog to extracting salt from evaporated seawater, this fundamental process has been a constant presence. However, a recent groundbreaking discovery by MIT researchers challenges our traditional understanding of evaporation. Their findings reveal that light, not just heat, plays a crucial role in driving this phenomenon.
Light-triggered evaporation
This research, published in the journal PNAS, sheds light on a previously unknown mechanism – the photomolecular effect. The MIT team, led by Professor Gang Chen, demonstrated that light striking the water's surface can directly liberate water molecules, causing them to evaporate into the air. This effect occurs independently of heat, upending our long-held belief that thermal energy is the sole driver of evaporation.



