
Breaking News
 Why Doug Band's Upcoming Testimony to House Oversight on the Epstein Investigation...
Why Doug Band's Upcoming Testimony to House Oversight on the Epstein Investigation...
 Iran War Day Four: Shifting US Narratives As Skepticism Grows
Iran War Day Four: Shifting US Narratives As Skepticism Grows
 Age Verification Mandates: The 'Protect the Kids' Scam That's Building a Permanent Surve
Age Verification Mandates: The 'Protect the Kids' Scam That's Building a Permanent Surve
Top Tech News
 US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
 Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
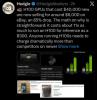 H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
 We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
 She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
 A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
 DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
 Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
 WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
Scientists on Quest to Decode the Human Brain – And Read People's Minds
For the first time, the thoughts and impressions of people unable to communicate with the outside world were translated into continuous natural language, using a combination of artificial intelligence (AI) and brain imaging technology.
This is the closest science has yet come to reading someone's mind. While advances in neuroimaging over the past two decades have enabled non-responsive and minimally conscious patients to control a computer cursor with their brain, HuthLab's research is a significant step closer towards accessing people's actual thoughts. As Alexander Huth, the neuroscientist who co-led the research, told the New York Times: "This isn't just a language stimulus. We're getting at meaning – something about the idea of what's happening. And the fact that's possible is very exciting."
Combining AI and brain-scanning technology, the team created a non-invasive brain decoder capable of reconstructing continuous natural language among people otherwise unable to communicate with the outside world. The development of such technology – and the parallel development of brain-controlled motor prosthetics that enable paralyzed patients to achieve some renewed mobility – holds tremendous prospects for people suffering from neurological diseases including locked-in syndrome and quadriplegia.
In the longer term, this could lead to wider public applications such as Fitbit-style health monitors for the brain and brain-controlled smartphones. On January 29, Elon Musk announced that his Neuralink tech startup had implanted a chip in a human brain for the first time. He had previously told followers that Neuralink's first product, Telepathy, would one day allow people to control their phones or computers "just by thinking".
But alongside such technological developments come major ethical and legal concerns. It's not only privacy but the very identity of people that may be at risk. As we enter this new era of so-called mind-reading technology, we will also need to consider how to prevent its potential to help people being outweighed by its potential to do harm.

 Geniuses on Education
Geniuses on Education
 RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?
RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?

