
Breaking News
 The Prostate Cancer Test Dilemma
The Prostate Cancer Test Dilemma
 The Separation of Righteousness and Politics
The Separation of Righteousness and Politics
 Russian strike knocks out power in Kyiv FRANCE 24 English
Russian strike knocks out power in Kyiv FRANCE 24 English
 CLAIM: Bitcoin is going to ZERO folks – HOLY SCHLIT! Benny Johnson and Mike Benz on it
CLAIM: Bitcoin is going to ZERO folks – HOLY SCHLIT! Benny Johnson and Mike Benz on it
Top Tech News
 How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
 Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
 Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
Researchers discover an effective non-opioid treatment for nerve pain
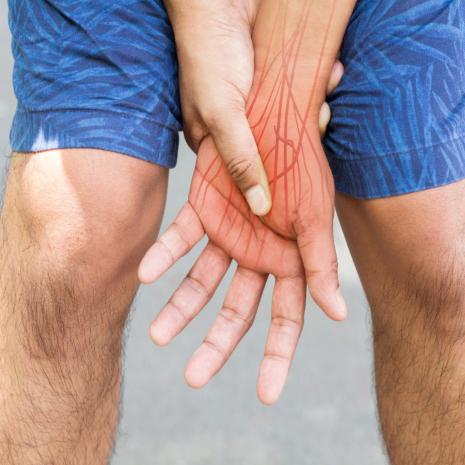
It's opened the door to developing a drug to treat the condition for which existing painkillers do little.
Diabetes, chemotherapy drugs, multiple sclerosis, injuries and amputations have all been associated with neuropathic pain, usually caused by damage to nerves in various body tissues, including the skin, muscles and joints. Mechanical hypersensitivity – or mechanical allodynia – is a major symptom of neuropathic pain, where innocuous stimuli like light touch cause severe pain.
Many available pain medications aren't effective in reducing this often-debilitating type of chronic pain. However, researchers at the University of Texas at Austin (UT Austin), in collaboration with UT Dallas and the University of Miami, may have advanced the treatment of neuropathic pain by discovering a molecule that reduces mechanical hypersensitivity in mice.
"We found it to be an effective painkiller, and the effects were rather long-lived," said Stephen Martin, a co-corresponding author of the study. "When we tested it on different models, diabetic neuropathy and chemotherapy-induced neuropathy, for example, we found this compound has an incredible beneficial effect."
The compound is FEM-1689, which binds to the sigma 2 receptor (σ2R), which was identified in 2017 as transmembrane protein 97 (TMEM97). The researchers had previously found that several small molecules that bind selectively to σ2R/TMEM97 produce strong and long-lasting anti-neuropathic pain effects in mice. FEM-1689, one such small molecule, was found to have improved selectivity for σ2R/TMEM97.



