
Breaking News
 The Prostate Cancer Test Dilemma
The Prostate Cancer Test Dilemma
 The Separation of Righteousness and Politics
The Separation of Righteousness and Politics
 Russian strike knocks out power in Kyiv FRANCE 24 English
Russian strike knocks out power in Kyiv FRANCE 24 English
Top Tech News
 How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
 Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
 Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
Nanoscale spinal implant helps restore mobility in paralyzed limbs
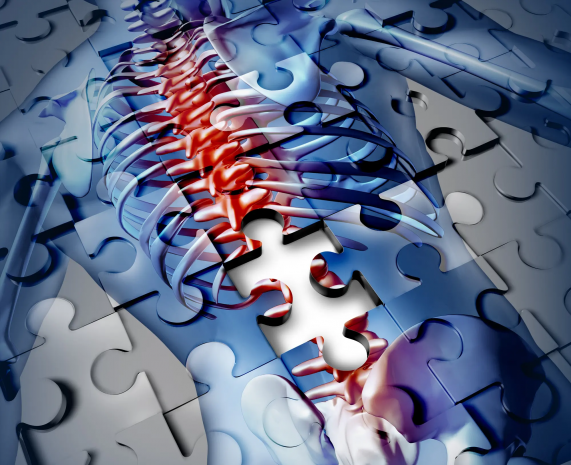
Spinal injuries interrupt the flow of electrical signals from the brain to the lower parts of the body, reducing mobility and in severe cases leading to total paralysis. Spinal stimulators are devices that can be surgically implanted into a patient's spine to bypass the injury site and restore some mobility. Unfortunately, these are often bulky, require surgery, and have precision issues.
For the new study, the Johns Hopkins team developed a much smaller device that's flexible and stretchable. It's placed into a different site than other stimulators – the ventrolateral epidural surface, which is not only close to motor neurons for better precision, but it can just be injected into place with a regular syringe, no surgery required. Tests in paralyzed mice proved promising.

 Pathway to the stars
Pathway to the stars

