
Breaking News
 China, India, US... 'the balance of power is changing': Musk
China, India, US... 'the balance of power is changing': Musk
 Cuba feels the pinch as US oil pressure drives food costs, blackouts and fuel shortages
Cuba feels the pinch as US oil pressure drives food costs, blackouts and fuel shortages
 ARGENTINA: Milei's Chainsaw Economic Model and The Illusion of Recovery
ARGENTINA: Milei's Chainsaw Economic Model and The Illusion of Recovery
 80,000 Toxins Every Day!! - The Deadly Truth About Your Food, Water, Skincare & Morning Joe!!
80,000 Toxins Every Day!! - The Deadly Truth About Your Food, Water, Skincare & Morning Joe!!
Top Tech News
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
 Lab–grown LIFE takes a major step forward – as scientists use AI to create a virus never seen be
Lab–grown LIFE takes a major step forward – as scientists use AI to create a virus never seen be
 New Electric 'Donut Motor' Makes 856 HP but Weighs Just 88 Pounds
New Electric 'Donut Motor' Makes 856 HP but Weighs Just 88 Pounds
 Donut Lab Says It Cracked Solid-State Batteries. Experts Have Questions.
Donut Lab Says It Cracked Solid-State Batteries. Experts Have Questions.
 Researchers who discovered the master switch that prevents the human immune system...
Researchers who discovered the master switch that prevents the human immune system...
Sun-run device turns dirty water into hydrogen fuel & drinking water
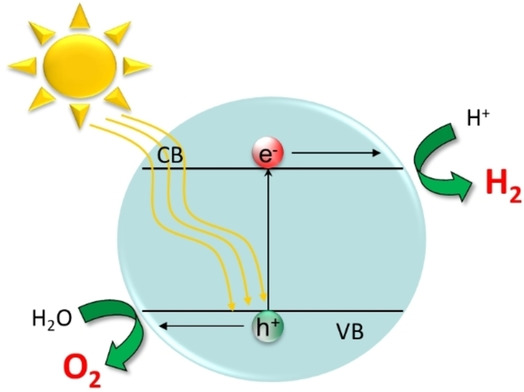
Because it works with any open water source and doesn't require external power, the device could be used in resource-limited or remote places.
Photocatalytic water splitting converts sunlight directly into storable hydrogen but often requires pure water and land for plant installation, while generating unusable waste heat. With water being a precious resource, a photocatalytic device that uses any untreated water source, such as a river, sea, water reservoir or industrial waste water, would be a more sustainable option.
So researchers from the University of Cambridge, inspired by the process of photosynthesis, created a solar-powered device capable of producing clean hydrogen fuel and clean drinking water simultaneously from polluted water or seawater.
"Bringing together solar fuels production and water production in a single device is tricky," said Chanon Pornrungroj, the study's lead author. "Solar-driven water splitting, where water molecules are broken down into hydrogen and oxygen, need to start with totally pure water because any contaminants can poison the catalyst or cause unwanted chemical side-reactions."
The researchers wanted to mimic a plant's ability to photosynthesize, but unlike previous devices that produced green hydrogen fuel from clean water sources, they wanted their device to use contaminated water, making it usable in regions where clean water is hard to find.
"In remote or developing regions, where clean water is relatively scarce and the infrastructure necessary for water purification is not readily available, water splitting is extremely difficult," said Ariffin Mohamad Annuar, a study co-author. "A device that could work using contaminated water could solve two problems at once: it could split water to make clean fuel, and it could make clean drinking water."

 The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives

