
Breaking News
 The Prostate Cancer Test Dilemma
The Prostate Cancer Test Dilemma
 The Separation of Righteousness and Politics
The Separation of Righteousness and Politics
 Russian strike knocks out power in Kyiv FRANCE 24 English
Russian strike knocks out power in Kyiv FRANCE 24 English
Top Tech News
 How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
 Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
 Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
Light therapy helps the brain clear out toxic Alzheimer's proteins
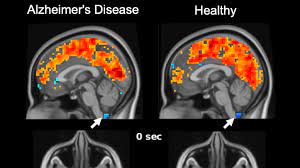
Despite their tireless efforts, researchers have been unable to develop a safe and effective way of treating Alzheimer's disease (AD) using pharmaceuticals, which has meant turning to non-pharmaceutical methods. A new study has demonstrated the therapeutic potential of light therapy, or phototherapy, in treating AD, showing promising results in mice that the researchers hope can be just as effective in humans. In the study, the researchers used photobiomodulation (PBM), a non-pharmaceutical therapy that employs red and near-infrared lights to stimulate the body to heal itself. There's evidence to suggest that PBM causes an increase in metabolism and microcirculation in the brain, in addition to reversing oxidative stress and inflammation. Recent studies discovered that PBM can stimulate the brain's lymphatic system to remove wastes and toxins.

 Pathway to the stars
Pathway to the stars

