
Breaking News
 Iran partially closes Strait of Hormuz, a vital oil choke point, as Tehran holds talks with U.S.
Iran partially closes Strait of Hormuz, a vital oil choke point, as Tehran holds talks with U.S.
 Lindsey Graham: 'US Soldiers Could Be Hit In War With Iran...But It's Worth It.'
Lindsey Graham: 'US Soldiers Could Be Hit In War With Iran...But It's Worth It.'
 It Begins: Mamdani Plans First NYC Property Tax Hike In Decades To Plug $5 Billion Hole
It Begins: Mamdani Plans First NYC Property Tax Hike In Decades To Plug $5 Billion Hole
 SpaceX Enters Secretive Pentagon Contest To Build Voice-Controlled Drone Swarm Tech: Report
SpaceX Enters Secretive Pentagon Contest To Build Voice-Controlled Drone Swarm Tech: Report
Top Tech News
 New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
 AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
 Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
 Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
 We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Your WiFi Can See You
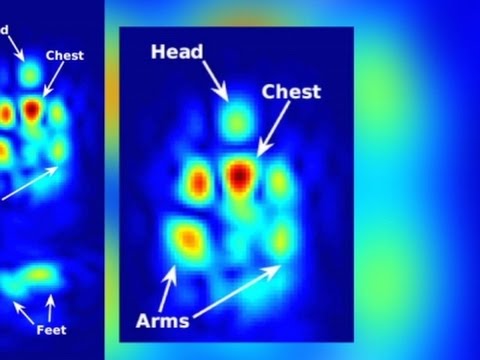
They found hot pockets in the house, which were used to obtain a search warrant and subsequently bust Kyllo.
Fortunately, a 5-4 Supreme Court decision ruled the scan an unlawful search under the Fourth Amendment, requiring a warrant the police did not obtain. Score one for privacy, but the government is about to have a far more controversial and dangerous tool at its disposal to monitor what's going on inside your home.
Unlike a thermal imager, this device is already in your home – and you put it there.
How It Works
WiFi is electromagnetic waves in the 2.4 and 5 GHz ranges. It's the same thing as the light you see, only it can penetrate walls due to its much longer wavelength. Just like light (and echolocation) these waves also reflect off various surfaces and, when reconstructed properly, can be used to create an image.
Development of this technology goes back at least as far as July 2005, where researchers claimed at an IEEE Symposium that they had created an ultra-wideband high-resolution short pulse imaging radar system operating around 10 GHz. The applications for which were explicitly for military and police use, providing them with "enhanced situation awareness."
A few years later, in 2008, researchers at UC Santa Barbara created an initial approach for imaging with WiFi that they presented at IEEE ACC 2009. A year later they demonstrated the feasibility of this approach.



