
Breaking News
 The Prostate Cancer Test Dilemma
The Prostate Cancer Test Dilemma
 The Separation of Righteousness and Politics
The Separation of Righteousness and Politics
 Russian strike knocks out power in Kyiv FRANCE 24 English
Russian strike knocks out power in Kyiv FRANCE 24 English
Top Tech News
 How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
 Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
 Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
Exercise's Secret for Preventing Alzheimer's Disease Discovered by Scientists
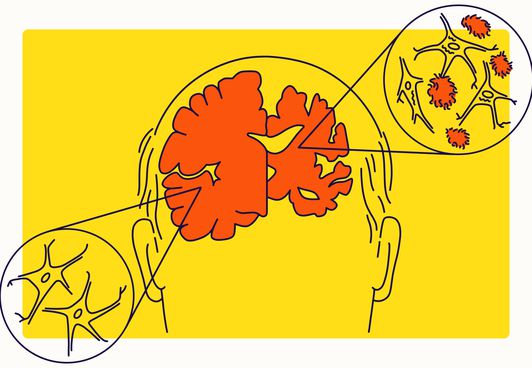
A new study has discovered why exercise may prevent Alzheimer's disease, potentially paving the way for new treatments for the currently incurable condition.
Experts at Massachusetts General Hospital found that during exercise, the body releases a hormone called irisin. This hormone has been shown to reduce the brain plaques and tangles commonly associated with Alzheimer's disease onset.
While physical exercise has consistently demonstrated its ability to reduce amyloid beta deposits in mouse experiments, the exact mechanisms remained unclear until now. The study, published in the journal Neuron, clears up this mystery and also suggests potential avenues for prevention and treatment of Alzheimer's — the most common form of dementia.
The Mass General team pioneered the development of the first 3D human cell culture models for Alzheimer's. These models showcase two primary characteristics of the disease: the formation of amyloid beta deposits and subsequent tau tangles in the brain.
It's well-documented that exercise elevates the levels of the muscle-derived hormone irisin, which not only helps regulate glucose and lipid metabolism in fat tissues but also enhances energy expenditure by promoting the conversion of white fat into brown fat. Earlier research indicated that irisin is present in both human and mouse brains. However, its levels are diminished in individuals with Alzheimer's. With this knowledge, the research team introduced irisin to their 3D cell culture model of Alzheimer's.

 Pathway to the stars
Pathway to the stars

