
Breaking News
 Silver's $3 Trillion Stress Test
Silver's $3 Trillion Stress Test
 BlackRock Just Confirmed the Worst-Case Scenario
BlackRock Just Confirmed the Worst-Case Scenario
 A COMEX report says JPMorgan closed its silver short around ~$78.
A COMEX report says JPMorgan closed its silver short around ~$78.
Top Tech News
 How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
 Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
 Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
Device Pulls Dozens of Liters of Water from the Air–Already Being Installed...
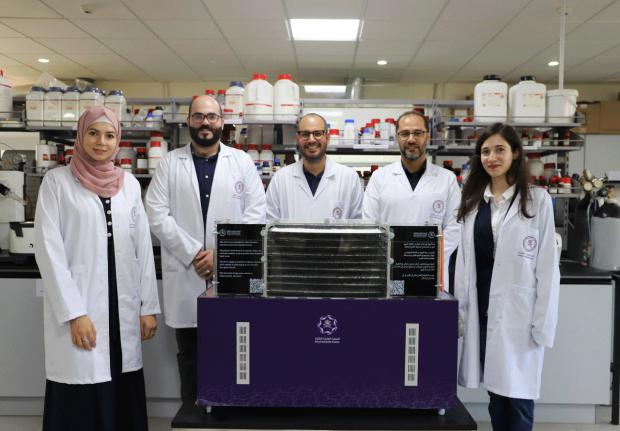

Entrepreneurs in Jordan have created a sophisticated machine that pulls water from the desert air at a rate that could cure the country's water woes.
1,000 units of their flagship device have already been pre-ordered by the Jordanian government, and the success of the invention has allowed the innovators to attract dozens of promising scientists who can hopefully expand on their success and bring water resources up to speed in the relatively-stable Near Eastern nation.
Jordan has an interesting contradiction of celebrating the highest academic involvement in the Arab world, but also suffering in one of its least-successful entrepreneurial landscapes and from a problem with water insecurity that ranks among the highest in the world.
Stepping up to address this problem is Aquaporo, a relatively straightforward, air conditioning-sized machine that can harvest 35 liters of water every day in a desert climate of 20% humidity.
Much of Jordan's population may only have access to 200 cubic meters of water per year, and only 36 hours of tap water per week provisioned by the authorities. The WHO warns these levels can create harm to human health and economic development.
Aquaporo CEO Kyle Cordova and engineering director Husam Almassad got their start at Jordan's Royal Scientific Society with a group of trainees. Their invention looked a bit like a chest freezer, but now more an A/C unit above a normal water cooler.
Inside, rows of nanomaterials formed into tubes and other shapes act like a sieve that filters water out of the air. The physics behind it are much the same as those found in this Classical Indian architectural feature and takes advantage of air's tendency to speed up as it moves through a narrow passageway; called the Venturi Effect.

 The Trump Show
The Trump Show 

