
Breaking News
 Can You Sell Gold and Silver Without Reporting to the IRS?
Can You Sell Gold and Silver Without Reporting to the IRS?
 Tulsi Gabbard to make surprise appearance at Nat. St. election officials meeting in Washington DC
Tulsi Gabbard to make surprise appearance at Nat. St. election officials meeting in Washington DC
 Can Trump s Fed Chair Choice Save the Dollar- With Phillip Patrick
Can Trump s Fed Chair Choice Save the Dollar- With Phillip Patrick
 Have Battleborn Batteries? Watch this! Safety Issue Update
Have Battleborn Batteries? Watch this! Safety Issue Update
Top Tech News
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
 Lab–grown LIFE takes a major step forward – as scientists use AI to create a virus never seen be
Lab–grown LIFE takes a major step forward – as scientists use AI to create a virus never seen be
 New Electric 'Donut Motor' Makes 856 HP but Weighs Just 88 Pounds
New Electric 'Donut Motor' Makes 856 HP but Weighs Just 88 Pounds
 Donut Lab Says It Cracked Solid-State Batteries. Experts Have Questions.
Donut Lab Says It Cracked Solid-State Batteries. Experts Have Questions.
Scientists Stumble on New Way to 'Hack' Photosynthesis For Renewable Energy
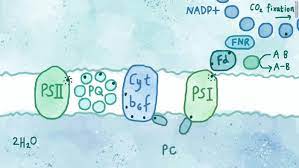
While trying to figure out if it were possible to extract electrons from a known process in the early stages of photosynthesis, the scientists instead found an entirely-new electron transfer pathway, which for those who remember their biology 101, is the metabolic method that extracts the most energy from food.
The study's authors believe this new understanding of photosynthesis could create new and more efficient ways of harnessing the process's power to generate biofuels.
The research team, comprised of scientists from across the globe, first set out to understand why a ring-shaped molecule called a 'quinone' is able to steal electrons from the photosynthetic process
Quinones, which are common in nature, are able to easily accept and give away electrons.



