
Breaking News
 The Prostate Cancer Test Dilemma
The Prostate Cancer Test Dilemma
 The Separation of Righteousness and Politics
The Separation of Righteousness and Politics
 Russian strike knocks out power in Kyiv FRANCE 24 English
Russian strike knocks out power in Kyiv FRANCE 24 English
Top Tech News
 How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
 Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
 Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
NASA's rotating detonation rocket engine posts record test results
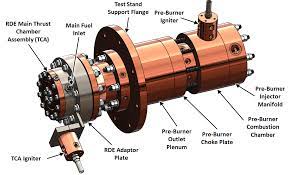
Combustion engines are tried and true, and however angry they might look and sound in a top-fuel dragster or space rocket booster, the combustion process of oxidizing fuel in air is relatively slow and predictable. Detonation, on the other hand, is as chaotic and destructive as it sounds. It's how most bombs work; you take an explosive fuel and hit it with a jolt of energy, and the chemical bonds holding each molecule together break apart, releasing wild amounts of energy in a shockwave that expands at supersonic speed.
NASA, along with many other groups, wants to harness these explosions for a couple of key reasons. Firstly, detonation engines have a considerably higher theoretical level of efficiency than combustion engines, perhaps as much as 25%; they should be able to produce more thrust using less fuel and a smaller rocket. In the engineering and economics of space flight, that means cheaper launches, more billable payload, and greater distances.

 Pathway to the stars
Pathway to the stars

