
Breaking News
 Powerful Pro-life Ad Set to Air During Super Bowl 'Adoption is an Option' (Video)
Powerful Pro-life Ad Set to Air During Super Bowl 'Adoption is an Option' (Video)
 Even in Winter, the Sun Still Shines in These Citrus Recipes
Even in Winter, the Sun Still Shines in These Citrus Recipes
 Dates: The Ancient Fertility Remedy Modern Medicine Ignores Amid Record Low Birth Rates
Dates: The Ancient Fertility Remedy Modern Medicine Ignores Amid Record Low Birth Rates
 Amazon's $200 Billion Spending Shock Reveals Big Tech's Centralization Crisis
Amazon's $200 Billion Spending Shock Reveals Big Tech's Centralization Crisis
Top Tech News
 How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
 Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
 Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
Lasers and ultrasound combine to pulverize arterial plaque
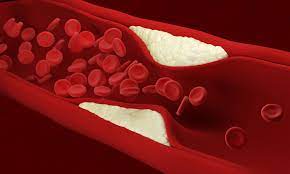
By bringing ultrasound into the mix, scientists at the University of Kansas have demonstrated a new take on this treatment that relies on exploding microbubbles to destroy plaque with greater safety and efficiency, while hinting at some unique long-term advantages.
The novel ultrasound-assisted laser technique builds off what's known as laser angioplasty, an existing treatment designed to improve blood flow in patients suffering from plaque buildup that narrows the arteries. Where more conventional treatments such as stents and balloon angioplasty expand the artery and compress the plaque, laser angioplasty destroys it to eliminate the blockage.
The laser is inserted into the artery with a catheter, and the thermal energy it generates turns water in the artery into a vapor bubble that expands, collapses and breaks up the plaque. Because this technique calls for high-power lasers, it has the potential to perforate or dissect the artery, something the scientists are looking to avoid by using low-power lasers instead.
They were able to do so in pork belly samples and ex vivo samples of artery plaque with the help of ultrasound. The method uses a low-power nanosecond pulsed laser to generate microbubbles, and applying ultrasound to the artery then causes these microbubbles to expand, collapse and disrupt the plaque.



