
Breaking News
 BREAKING: Federal Agents Descend on Suspected Somali Fraud Sites in Minneapolis (VIDEO)
BREAKING: Federal Agents Descend on Suspected Somali Fraud Sites in Minneapolis (VIDEO)
 BREAKING: Federal Agents Descend on Suspected Somali Fraud Sites in Minneapolis (VIDEO)
BREAKING: Federal Agents Descend on Suspected Somali Fraud Sites in Minneapolis (VIDEO)
 Aargh! Letters of marque would unleash Blackbeard on the cartels
Aargh! Letters of marque would unleash Blackbeard on the cartels
 How a Barter System Could Sustain Communities During a Supply Chain Collapse
How a Barter System Could Sustain Communities During a Supply Chain Collapse
Top Tech News
 EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
 This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
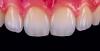 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
 Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Solar Panels That Make Electricity at Night are Finally Here - And They're Cheap...

About 750 million people in the world do not have access to electricity at night. Solar cells provide power during the day, but saving energy for later use requires substantial battery storage.
Researchers from Stanford University constructed a photovoltaic cell that harvests energy from the environment during the day and night, avoiding the need for batteries altogether. The device makes use of the heat leaking from Earth back into space—energy that is on the same order of magnitude as incoming solar radiation.
"You want the thermoelectric to have very good contact with both the cold side, which is the solar cell, and the hot side, which is the ambient environment," said author Sid Assawaworrarit. "If you don't have that, you're not going to get much power out of it."
At night, solar cells radiate and lose heat to the sky, reaching temperatures a few degrees below the ambient air. The device under development uses a thermoelectric module to generate voltage and current from the temperature gradient between the cell and the air. This process depends on the thermal design of the system, which includes a hot side and a cold side.



