
Breaking News
DRINK 1 CUP Before Bed for a Smaller Waist
 Nano-magnets may defeat bone cancer and help you heal
Nano-magnets may defeat bone cancer and help you heal
 Dan Bongino Officially Leaves FBI After One-Year Tenure, Says Time at the Bureau Was...
Dan Bongino Officially Leaves FBI After One-Year Tenure, Says Time at the Bureau Was...
 WATCH: Maduro Speaks as He's Perp Walked Through DEA Headquarters in New York
WATCH: Maduro Speaks as He's Perp Walked Through DEA Headquarters in New York
Top Tech News
 Laser weapons go mobile on US Army small vehicles
Laser weapons go mobile on US Army small vehicles
 EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
 This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Methane-Eating Bacteria Converts Greenhouse Gas to Fuel (And Could Clean-up Fracking Sites)
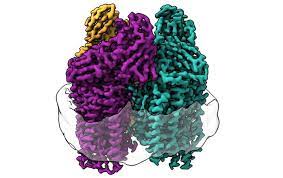
Yet we know very little about how the complex reaction occurs, limiting our ability to use the double benefit to our advantage.
By studying the enzyme the bacteria use to catalyze the reaction, a team at Northwestern University now has discovered key structures that may drive the process.
Their findings ultimately could lead to the development of human-made biological catalysts that convert methane gas into methanol.
"Methane has a very strong bond, so it's pretty remarkable there's an enzyme that can do this," said Northwestern's Amy Rosenzweig, senior author of the paper. "If we don't understand exactly how the enzyme performs this difficult chemistry, we're not going to be able to engineer and optimize it for biotechnological applications."
The enzyme, called particulate methane monooxygenase (pMMO), is a particularly difficult protein to study because it's embedded in the cell membrane of the bacteria.



