
Breaking News
 Powerful Pro-life Ad Set to Air During Super Bowl 'Adoption is an Option' (Video)
Powerful Pro-life Ad Set to Air During Super Bowl 'Adoption is an Option' (Video)
 Even in Winter, the Sun Still Shines in These Citrus Recipes
Even in Winter, the Sun Still Shines in These Citrus Recipes
 Dates: The Ancient Fertility Remedy Modern Medicine Ignores Amid Record Low Birth Rates
Dates: The Ancient Fertility Remedy Modern Medicine Ignores Amid Record Low Birth Rates
 Amazon's $200 Billion Spending Shock Reveals Big Tech's Centralization Crisis
Amazon's $200 Billion Spending Shock Reveals Big Tech's Centralization Crisis
Top Tech News
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
 Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Kidney stones blasted by new non-surgical sound wave device
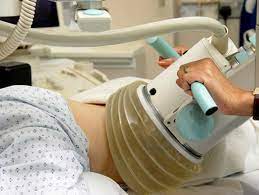
The method, dubbed burst wave lithotripsy (BWL), successfully fragmented the majority of kidney stones, promising a non-surgical way to treat patients with this common condition.Up to 15 percent of people will experience kidney stones at some point in their life. Many cases of small stones are known to pass spontaneously and without any intervention, however, some patients require surgical intervention to avoid permanent kidney damage.For several decades surgeons have used sound waves to break up kidney stones in a method called extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL). The method involves high intensity acoustic pulses and generally requires patients to be sedated or even anesthetized.

 Smart dust technology...
Smart dust technology...

