
Breaking News
 Powerful Pro-life Ad Set to Air During Super Bowl 'Adoption is an Option' (Video)
Powerful Pro-life Ad Set to Air During Super Bowl 'Adoption is an Option' (Video)
 Even in Winter, the Sun Still Shines in These Citrus Recipes
Even in Winter, the Sun Still Shines in These Citrus Recipes
 Dates: The Ancient Fertility Remedy Modern Medicine Ignores Amid Record Low Birth Rates
Dates: The Ancient Fertility Remedy Modern Medicine Ignores Amid Record Low Birth Rates
 Amazon's $200 Billion Spending Shock Reveals Big Tech's Centralization Crisis
Amazon's $200 Billion Spending Shock Reveals Big Tech's Centralization Crisis
Top Tech News
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
 Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Causing a buzz: Insect-inspired robot weighs just 0.01lbs and can fly at 1.6mph...
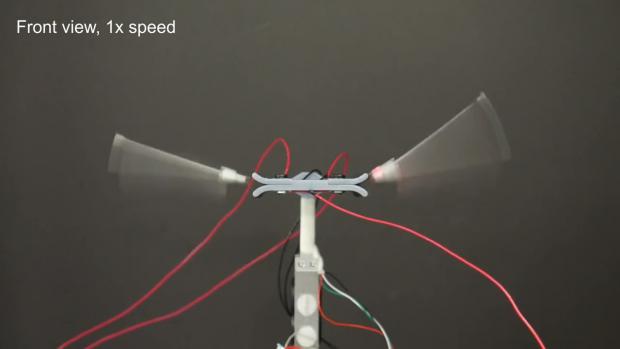
An insect-inspired flying robot with wings that buzz thanks to a new type of electric 'muscle' has been developed by British scientists.
The prototype weighs about 0.01lbs (5g), has a wing span of 5.9 inches (15cm) and can fly at 1.6mph.
It is hoped that one day the robot will be able to look for survivors in disaster zones such as collapsed buildings, monitor hard-to-reach infrastructure and pollinate crops.
Researchers at Bristol University said its wings are so efficient that they actually provide more power than an insect muscle of the same weight.
'It's very challenging to beat nature,' Dr Tim Helps, lead author of the study, told MailOnline.
'If we can produce more power than insect muscle, it means that we can potentially have better performance than an insect — which is really exciting.'
He added: 'It's very challenging because nature does such an amazing job.'
Until now, typical micro flying robots have used motors, gears and other complex transmission systems to achieve the up-and-down motion of the wings.
However, researchers involved in the study said this had added complexity, weight and undesired dynamic effects.
Instead, after taking inspiration from bees and other flying insects, they created an artificial muscle system called the liquid-amplified zipping actuator (Laza), which achieves wing motion using no rotating parts or gears.
The wing itself acts like a negatively charged electrode, while above and below it are two positively charged electrodes.

 Smart dust technology...
Smart dust technology...

