
Breaking News
 Powerful Pro-life Ad Set to Air During Super Bowl 'Adoption is an Option' (Video)
Powerful Pro-life Ad Set to Air During Super Bowl 'Adoption is an Option' (Video)
 Even in Winter, the Sun Still Shines in These Citrus Recipes
Even in Winter, the Sun Still Shines in These Citrus Recipes
 Dates: The Ancient Fertility Remedy Modern Medicine Ignores Amid Record Low Birth Rates
Dates: The Ancient Fertility Remedy Modern Medicine Ignores Amid Record Low Birth Rates
 Amazon's $200 Billion Spending Shock Reveals Big Tech's Centralization Crisis
Amazon's $200 Billion Spending Shock Reveals Big Tech's Centralization Crisis
Top Tech News
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
 Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
World's tiniest camera -- the size of a grain of salt -- created by scientists
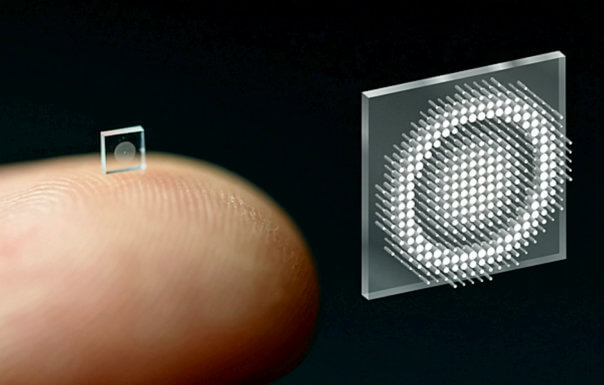
Computer scientists from Princeton University and the University of Washington say the small device they created can take crisp, full-color pictures just as well as conventional cameras which are 500,000 times bigger.
The new technology may help doctors to diagnose and treat diseases far less invasively than traditional endoscopy can today. It will also make imaging better, as thousands of tiny devices could cover the whole surface of a smartphone to become one giant camera — instead of mobile devices needing three different cameras to take pictures.
Traditional cameras use several curved glass or plastic lenses to bend light rays into focus, but the new device uses a "metasurface" which developers can make just like a computer chip. The metasurface is just half a millimeter wide and is made up of 1.6 million tiny posts, which are all shaped like cylinders but none of them look exactly the same.
When the antennae-like tiny posts interact with light, with the help of algorithms, they produce better pictures and capture a wider frame of view than any full-color metasurface camera created so far. The metasurfaces are made from silicon nitride, a glass-like material which can be manufactured easily and produced more cheaply than lenses in conventional cameras.
Older metasurfaces took poor pictures
Senior study author Dr. Felix Heide notes that a key innovation during the camera's development was figuring out how to combine the design of the optical surface with the signal processing algorithms that make an image.
The team adds that this integrated design boosted the camera's performance in natural light. Previous metasurface cameras have required the pure laser light of a laboratory or other ideal conditions in order to create high-quality images.

 Smart dust technology...
Smart dust technology...

