
Breaking News
 Aaron Day on Bitcoin and Stable Coins: 'The Creature From Epstein Island'
Aaron Day on Bitcoin and Stable Coins: 'The Creature From Epstein Island'
 Elon Musk: They put like 500 or 600 January 6th protesters in prison, and not one person...
Elon Musk: They put like 500 or 600 January 6th protesters in prison, and not one person...
 Cuba Willing to Talk to US, But Not Under Pressure
Cuba Willing to Talk to US, But Not Under Pressure
Top Tech News
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
 Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Early Beamed Microwave-Powered Rocket Launches and Drone Power
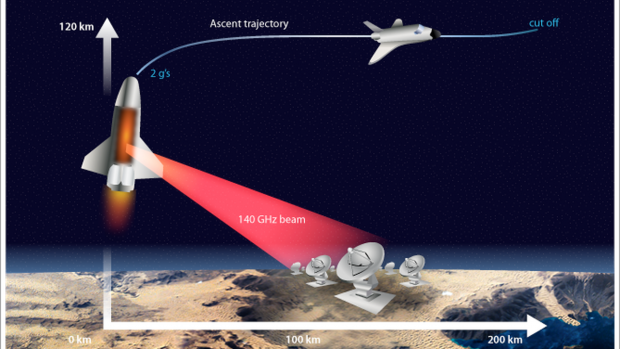
This limitation could be overcome by wirelessly transmitting the needed power to the rocket through a beam of microwave radiation. A research team from Japan has investigated the viability of using such microwave-powered propulsion for real-world applications.
In a study published this month in the Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, researchers led by the University of Tsukuba have demonstrated wireless power transmission via microwaves for a free-flying drone and determined the efficiency of this process.
Previous analyses of this kind were carried out decades ago and mostly considered microwaves of a low frequency (a few gigahertz; GHz). Given that the power transmission efficiency increases as the operating frequency is raised, the team behind this latest research used microwaves with a relatively high frequency (28 GHz). The team's drone weighed roughly 0.4 kilograms and hovered for 30 seconds at a height of 0.8 meters above the source of the microwave beam.
The researchers measured the efficiencies of the power transfer through the beam (4%), the capture of microwaves by the drone (30%), the conversion of microwaves to electricity for propulsion (40%), and other relevant processes. Based on this information and an analytical formula, they calculated the overall power transmission efficiency in their experiment to be 0.43%. For comparison, in a previous study, the team measured the total transmission efficiency for a fixed-position (rather than free-flying) drone to be 0.1%.
"These results show that more work is needed to improve the transmission efficiency and thoroughly evaluate the feasibility of this propulsion approach for aircraft, spacecraft, and rockets," explains Shimamura. "Future studies should also aim to refine the beam-tracking system and increase the transmission distance beyond that demonstrated in our experiment."
Although microwave-powered rocket propulsion is still in its early stages, it could someday become a superior way to launch rockets into orbit given the high onboard-fuel demands of conventional propulsion techniques.

 Why We'll Win
Why We'll Win
 Smart dust technology...
Smart dust technology...

