
Breaking News
 Closing in on How Charlie Kirk Was Assassinated
Closing in on How Charlie Kirk Was Assassinated
 Here's a little song I just wrote. Dedicated to Al Gore.
Here's a little song I just wrote. Dedicated to Al Gore.
 Judge Blocks Executive Order Tightening Voter-registration Requirements
Judge Blocks Executive Order Tightening Voter-registration Requirements
 ALEX JONES' EXCLUSIVE EPSTEIN DOJ MEGA DOCUMENT DUMP ANALYSIS:
ALEX JONES' EXCLUSIVE EPSTEIN DOJ MEGA DOCUMENT DUMP ANALYSIS:
Top Tech News
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
 Lab–grown LIFE takes a major step forward – as scientists use AI to create a virus never seen be
Lab–grown LIFE takes a major step forward – as scientists use AI to create a virus never seen be
 New Electric 'Donut Motor' Makes 856 HP but Weighs Just 88 Pounds
New Electric 'Donut Motor' Makes 856 HP but Weighs Just 88 Pounds
 Donut Lab Says It Cracked Solid-State Batteries. Experts Have Questions.
Donut Lab Says It Cracked Solid-State Batteries. Experts Have Questions.
The 'holy grail' of batteries:
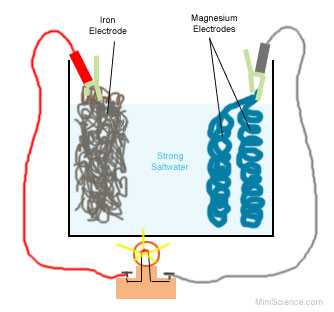
An 'iron-air' battery has been developed in the US that can store electricity from wind or solar power stations for days at a time, slowly discharging it to the grid.
It will help tackle climate change by reducing the need for fossil fuel power plants, according to technology startup Form Energy, from Massachusetts, US.
The Iron-Air battery is a 'new class of cost-effective, multi-day energy storage system,' that can feed electricity for 100 hours at 1/10th the cost of lithium-Ion, the 'holy grail' in terms of renewable energy technology.
It is made using iron, one of the most common elements on Earth, and works by breathing in oxygen, converting iron to rust, and turning rust back to iron.
As it takes in the oxygen and converts the iron back and forth it is charging and discharging the battery, a process that keeps the energy stored for a longer period.
The batteries are too heavy for use in electric cars, according to the firm, who say they are designed to meet the challenge of keeping a constant power supply.
If development continues at pace, Form Energy hope the first batteries will be working to supply the grid by 2025.
This will solve one of the most elusive problems facing renewable energy, that is how to cheaply store large amounts of electricity and supply it to power grids when the sun isn't shining for solar panels or wind isn't blowing for turbines.
Solar and wind resources are the lowest marginal cost sources of electricity in most of the world, but they don't provide a constant supply like fossil fuel power plants.



