
Breaking News
 After Trump Meeting, Slovak PM Fico Says 'EU Is Not Taken Seriously' By World Leaders
After Trump Meeting, Slovak PM Fico Says 'EU Is Not Taken Seriously' By World Leaders
 US NatGas Poised For Biggest Weekly Spike On Record As "Blizzard Of '96" Fears Resurfa
US NatGas Poised For Biggest Weekly Spike On Record As "Blizzard Of '96" Fears Resurfa
 Police Use Tear Gas, Stun Grenades Against Farmers Protesting Mercosur Trade Agreement At EU...
Police Use Tear Gas, Stun Grenades Against Farmers Protesting Mercosur Trade Agreement At EU...
 Supreme Court Seems Skeptical Over Lisa Cook Firing
Supreme Court Seems Skeptical Over Lisa Cook Firing
Top Tech News
 The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
The day of the tactical laser weapon arrives
 'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
'ELITE': The Palantir App ICE Uses to Find Neighborhoods to Raid
 Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
Solar Just Took a Huge Leap Forward!- CallSun 215 Anti Shade Panel
 XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
XAI Grok 4.20 and OpenAI GPT 5.2 Are Solving Significant Previously Unsolved Math Proofs
 Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
Watch: World's fastest drone hits 408 mph to reclaim speed record
 Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
Ukrainian robot soldier holds off Russian forces by itself in six-week battle
 NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
 Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
 The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
Ultralight armor material made of tiny carbon struts outperforms Kevlar
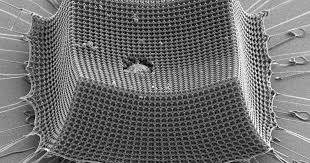
The latest example comes from material scientists at MIT, who have used advanced nanoscale engineering to craft a new armor material they say outperforms Kevlar and steel.
The starting point for the promising new material was a photosensitive resin, which was treated with lasers to form a lattice pattern made up of repeating microscopic struts. This material was then put in a high-temperature vacuum chamber, which converted the polymer into an ultralight carbon with an architecture originally inspired by special foams designed to absorb impacts.
"Historically this geometry appears in energy-mitigating foams," says lead author, Carlos Portela. "While carbon is normally brittle, the arrangement and small sizes of the struts in the nanoarchitected material gives rise to a rubbery, bending-dominated architecture."

 Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market
Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market


