
Breaking News
 One company does over 50% of all school photos in America and over 25% of school photos globally
One company does over 50% of all school photos in America and over 25% of school photos globally
 Your Water Filter Will Clog - The Medieval Sand Filtration System That Purifies Forever
Your Water Filter Will Clog - The Medieval Sand Filtration System That Purifies Forever
 Aaron Day - BTC and Stable Coins: 'The Creature From Epstein Island' (Publisher Recommended)
Aaron Day - BTC and Stable Coins: 'The Creature From Epstein Island' (Publisher Recommended)
Top Tech News
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
 Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Cellular Imaging from Phonon Imaging on a Fiber Probe
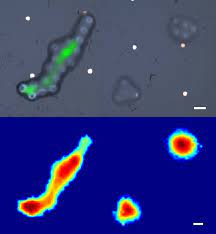
The new technology produces microscopic and nanoscopic resolution images that will one day help clinicians to examine cells inhabiting hard-to-reach parts of the body, such as the gastrointestinal tract, and offer more effective diagnoses for diseases ranging from gastric cancer to bacterial meningitis.
Nature Light Science and Applications- Phonon imaging in 3D with a fibre probe
Abstract
We show for the first time that a single ultrasonic imaging fibre is capable of simultaneously accessing 3D spatial information and mechanical properties from microscopic objects. The novel measurement system consists of two ultrafast lasers that excite and detect high-frequency ultrasound from a nano-transducer that was fabricated onto the tip of a single-mode optical fibre. A signal processing technique was also developed to extract nanometric in-depth spatial measurements from GHz frequency acoustic waves, while still allowing Brillouin spectroscopy in the frequency domain. Label-free and non-contact imaging performance was demonstrated on various polymer microstructures. This singular device is equipped with optical lateral resolution, 2.5 μm, and a depth-profiling precision of 45 nm provided by acoustics. The endoscopic potential for this device is exhibited by extrapolating the single fibre to tens of thousands of fibres in an imaging bundle. Such a device catalyses future phonon endomicroscopy technology that brings the prospect of label-free in vivo histology within reach.

 Why We'll Win
Why We'll Win
 Smart dust technology...
Smart dust technology...

