
Breaking News
 One company does over 50% of all school photos in America and over 25% of school photos globally
One company does over 50% of all school photos in America and over 25% of school photos globally
 Your Water Filter Will Clog - The Medieval Sand Filtration System That Purifies Forever
Your Water Filter Will Clog - The Medieval Sand Filtration System That Purifies Forever
 Aaron Day - BTC and Stable Coins: 'The Creature From Epstein Island' (Publisher Recommended)
Aaron Day - BTC and Stable Coins: 'The Creature From Epstein Island' (Publisher Recommended)
Top Tech News
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
 Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
Study Shows Vaporizing E-Waste Makes it Easy to Recover Precious Metals at 13-Times Lower Costs
MONKEY ME, MONKEY YOU First part-human, part-monkey embryo created by scientists sparks outcry
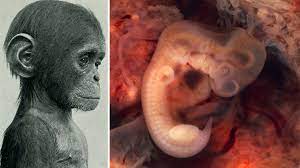
Researchers have grown human stem cells in monkey embryos to try and better understand how the cells communicate.
Some people are totally against this kind of experimentation and think it could lead the way to "human-nonhuman" creatures.
The controversial embryos were made at the Salk Institute in California.
They're scientifically known as monkey-human chimeras.
Human stem cells, known for the ability to become different types of cells, were injected into macaque embryos in a petri dish.
The scientists hope their work could be used to create organs for transplants and teach us more about human development and disease progression.
Professor Juan Carlos Izpisua Belmonte led the research.
He also worked on the first human-pig hybrid in 2017.
He said: "These chimeric approaches could be really very useful for advancing biomedical research not just at the very earliest stage of life, but also the latest stage of life."
The human and macaque monkey embryos were monitored for around 20 days and have since been destroyed.

 Why We'll Win
Why We'll Win
 Smart dust technology...
Smart dust technology...

